Service Information for Testing the Inhibitory Efficacy of Alpha-Glucosidase (α-glycosidase) Enzyme
VISBIO offers services for testing and analyzing the inhibitory effects on the enzyme alpha-glucosidase. This enzyme is essential in the development of diabetes mellitus, a disease caused by abnormalities in insulin secretion, leading to high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia). Currently, the number of diabetes patients is increasing rapidly. The general approach to treating diabetes involves dietary control, exercise, and insulin injections when necessary. For many patients, physicians prescribe medications that work by reducing or preventing the absorption of glucose, such as acarbose, miglitol, and voglibose. These medications function by inhibiting the activity of alpha-amylase and alpha-glucosidase enzymes, which play crucial roles in the hydrolysis of starch into glucose. As a result, the absorption of glucose from the small intestine into the bloodstream decreases.
However, long-term use of these medications may lead to unwanted side effects, such as hepatotoxicity. To address this issue, researchers have been searching for herbal remedies that possess the ability to inhibit the activity of alpha-glucosidase, aiming to improve treatment efficacy and minimize adverse effects on patients.
Diabetes and the origin of Alpha-glucosidase
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a disease that results from abnormalities in insulin hormone secretion, leading to high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia). Currently, the number of diabetes patients is rapidly increasing, prompting the World Health Organization (WHO) to address this issue seriously. Diabetes patients are at a higher risk of developing severe complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and if infected with the coronavirus (COVID-19), they can face life-threatening consequences. Therefore, the general approach to treating diabetes involves controlling diet and physical activity, and in some cases, insulin injections.
For those with more severe cases, physicians often prescribe medications that work by reducing or preventing the absorption of glucose, such as acarbose, miglitol, and voglibose. These drugs act by inhibiting the activity of the enzymes alpha-amylase and alpha-glucosidase, which play crucial roles in accelerating the hydrolysis of starch into glucose, thereby reducing the absorption of glucose from the small intestine into the bloodstream. However, prolonged use of medications in this category can lead to adverse effects on patients, such as liver toxicity and undesirable gastrointestinal symptoms like bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea. Moreover, type 2 diabetes patients may require long-term treatment and often need a combination of multiple drugs. Due to these reasons, there is a need to search for new naturally occurring alpha-amylase and alpha-glucosidase inhibitors to enhance treatment effectiveness and minimize unwanted side effects on the body.
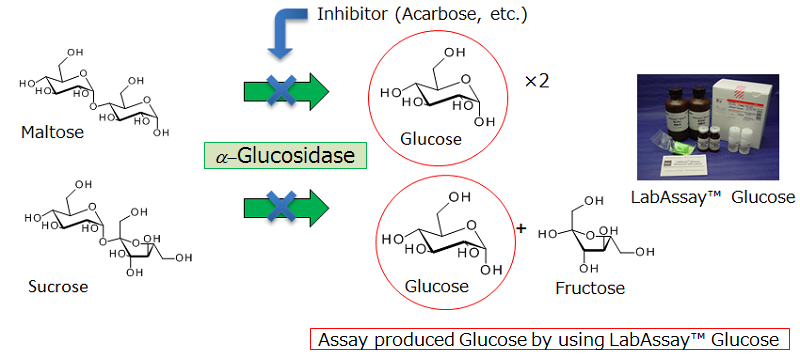
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitory assay
Alpha-glucosidase is an enzyme located on the cell wall of the small intestine. Its function is to break down starch and carbohydrates into single molecules of sugar, such as glucose, through enzymatic hydrolysis. This allows the body to absorb glucose into the bloodstream and supply it to various cells throughout the body. Therefore, inhibiting the action of alpha-glucosidase is another way to delay or prevent the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream, resulting in reduced blood sugar levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
The following is an example of a report on the effectiveness of alpha-glucosidase inhibition
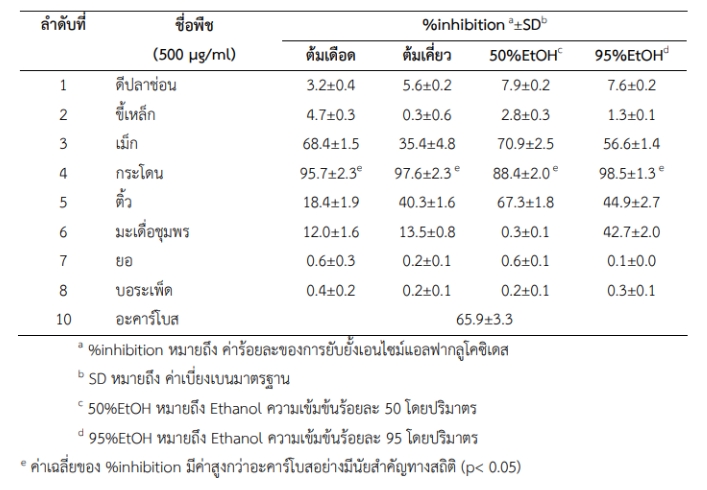
Table: Test Results of Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity in Traditional Herbal Extracts
In a study conducted by Tanika et al. (2021), several types of traditional medicinal plants were investigated for their alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activity using different extraction methods, including boiling, simmering, and extraction with 50% EtOH and 95% EtOH. The results showed significant inhibitory effects (% inhibition) on alphaglucosidase as follows: Among the plant extracts obtained through boiling and EtOH extraction at all concentrations, the highest % inhibition was observed in the extracts of ‘Kradoen,’ ‘Mak,’ and ‘Tiew,’ respectively, followed by the extracts obtained through simmering, with the highest % inhibition found in the extracts of ‘Kradoen,’ ‘Tiew,’ and ‘Mak,’ respectively. Notably, the ‘Kradoen’ extract obtained through 95% EtOH extraction exhibited the highest % inhibition at 98.5±1.3. Therefore, the ‘Kradoen’ extract obtained through 95% EtOH extraction is considered promising for further research and development as a herbal remedy for diabetes.
Literature:
- พรชนก ชโลปกรณ์ และ พงศธร กล่อมสกุล, 2017, ฤทธิ์ในการยับยั้งแอลฟาอะไมเลสและแอลฟากลูโคซิเดสของสารสกัดฝาง ม้ากระทืบโรง และปลาไหลเผือก, วารสารวิจัยราชภัฏพระนคร สาขาวิทยาศาสตร์และเทคโนโลยี ปีที่ 12 ฉบับที่ 1, 63-73.
- วชิยา ไตรบุญ, 2558, การศึกษาโครงสร้างและฤทธิ์ในการยับยั้งการทำงานของเอนไซม์แอลฟากลูโคซิเดส จากองค์ประกอบทางเคมีของเหง้าว่านนางคำ, บัณฑิตวิทยาลัย มหาวิทยาลัยศิลปากร.
- ทัณฑิกา แก้วสูงเนิน,ฉัตรชนก นุกูลกิจ, เพ็ญศิริ จันทร์แอ, ภานิชา พงศ์นราทร, นฤวัตร ภักดี, พิเชษฐ เวชวิฐาน, ศรัณย์ ฉวีรักษ์, อนรรฆอร จิตต์เจริญธรรม, ปภาวินี ผะแดนนอก และฉัตรลดา หงษ์วิลัย, 2564, การยับยั้งการทำงานของเอนไซม์แอลฟากลูโคซิเดสของสารสกัด สมุนไพรพื้นบ้านในจังหวัดสกลนคร, วารสารหมอยาไทยวิจัย ปีที่ 7 ฉบับที่ 1, 15-28.
- วิมลพรรณ รุ่งพรหม,ศิริรัตน์ ศิริพรวิศาล, สัญญา เขียวไสว และ มุกดา ทรงไตรย์, 2553, สารยับยั้งแอลฟากลูโคซิเดสจากพืชสมุนไพรเพื่อใช้บำบัดโรคเบาหวาน, ว.วิทย์. กษ. 41(3/1)(พิเศษ):301-304.