Service Information for Curcuminoid in Turmeric Analysis and Testing
VISBIO offers a service for the examination and analysis of biomarker quantities of curcuminoids in all health and beauty products. Turmeric, a herbal plant, contains significant substances that have beneficial effects on health. From pharmacological research, it has been found that important compounds in turmeric possess antiinflammation, anti-cancer, antimicrobial, and antioxidant properties, which can contribute to the prevention or treatment of certain diseases.
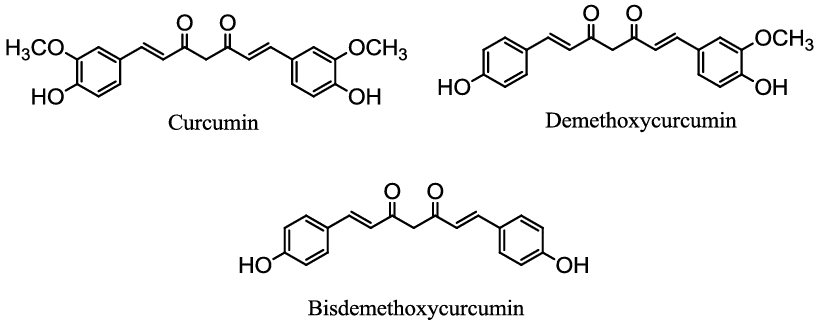
These properties are attributed to a group of curcuminoids, namely Curcumin, Demethoxycurcumin, and Bisdemethoxycurcumin, which have various benefits in the health and beauty industry. As a result, turmeric is increasingly utilized in the production of medicines, cosmetics, and dietary supplements.
Turmeric
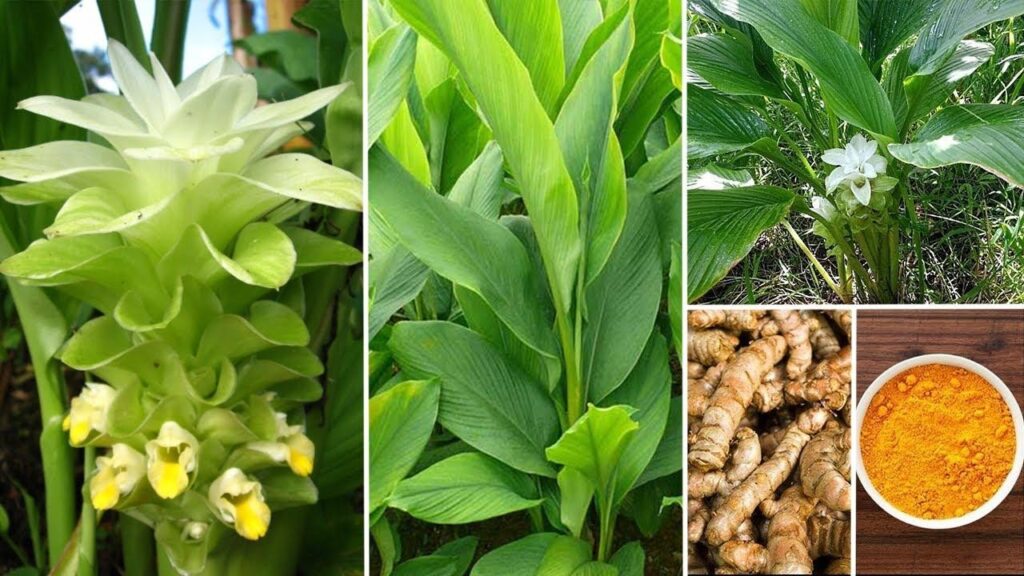
Turmeric, or Curcuma longa L. (Zingiberaceae), originated in India and has spread throughout tropical and subtropical regions of the world. It is widely cultivated in Asia, including Southeast Asia, and belongs to the same family as ginger and galangal. Turmeric is a rhizomatous plant, meaning it has underground stems or roots. The flesh of the rhizome is yellow, while the above-ground parts, such as the stems, leaves, and flowers, are found above the ground. The flowers are whitish-yellow and form spike-like inflorescences, with the flower stalk directly emerging from the rhizome. The numerous large petal-like bracts are green with pinkish tones on the upper part, darker than the lower part.
In Thailand, turmeric is popularly grown as a vegetable in kitchen gardens, and its roots or rhizomes are used as a spice in food preparation. In some regions, it is known as “kamin kaeng,” “ki-min,” “tai,” “saiyo,” or “Tayo.” Besides the underground stems or rhizomes of turmeric, the plant also has other uses.
Turmeric contains important compounds that have positive effects on health, helping to prevent or treat certain diseases. Pharmacological studies have revealed that turmeric contains essential properties such as anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, antimicrobial, and antioxidant effects. These properties are attributed to the presence of curcuminoids, a group of chemicals found in turmeric.
Curcuminoid
Curcuminoid is composed of three types of compounds: Curcumin, Demethoxycurcumin, and Bisdemethoxycurcumin.
Currently, herbal medicine has gained more interest in its use as medicine, cosmetics, and dietary supplements. Thailand, which has various medicinal plants with beneficial properties, is suitable for further development and incorporation into the production process of products. Additionally, the government also promotes the use of herbal medicine as a substitute for current medications and supports the herbal medicine industry for exportation to other countries.
Turmeric is an ingredient filled with benefits for the skin and is widely used in cosmetic products.
“Turmeric” is considered a Thai herb dating back to ancient times. Curcuminoids are yellow-orange pigments found in turmeric, and they possess antioxidant properties, anti-inflammatory properties, and antimicrobial properties. Apart from these benefits, turmeric is also popularly used in cosmetics. People in Southeast Asia and the Far East have used turmeric for facial application to make the skin soft and supple. In Malaysia and ancient Thailand, turmeric was used in baths to improve skin complexion, resulting in radiant and clear skin, reducing blemishes, dark spots, and blackheads effectively. Monoterpenoids are another group of substances found in turmeric, known for the following properties:
- Antioxidant properties: Curcuminoids from turmeric have higher antioxidant properties compared to vitamin C.
- Skin protection and wrinkle reduction: Turmeric contains numerous curcuminoids and phytosterols that possess potent antioxidant properties, which help delay the appearance of wrinkles.
- Inhibition of tyrosinase enzyme: Curcumin in turmeric inhibits the tyrosinase enzyme responsible for melanin production, which causes darkening of the skin.
- Anti-acne properties: The essential oil and curcumin in turmeric have properties that inhibit Propionibacterium acnes, the bacteria responsible for acne.
- Anti-inflammatory properties: Curcumin has anti-inflammatory properties that reduce skin inflammation.
Turmeric is also used for body nourishment and is suitable for use in dietary supplements.
“Curcuma longa” or “turmeric” can treat digestive problems due to its distinctive taste and color. It has a spicy and slightly bitter taste, making it suitable as a seasoning or coloring agent in various products and is extracted to produce aromatic oil.
The root or rhizome of turmeric is traditionally used as medicine. Turmeric has health benefits as a natural antiinflammatory agent, aiding in the repair of damaged tissues and promoting overall bodily strength. Curcumin, the essential yellow compound, has been extensively researched and found to have numerous health benefits, such as treating and preventing various diseases, including arthritis, inflammation, diarrhea, inhibiting Helicobacter pylori infections, indigestion, and reducing cholesterol levels. Turmeric also helps with skin inflammation, headaches, and more.
In summary, turmeric is a valuable herb with numerous benefits for the skin and health, making it an essential ingredient in cosmetic products and traditional medicine.
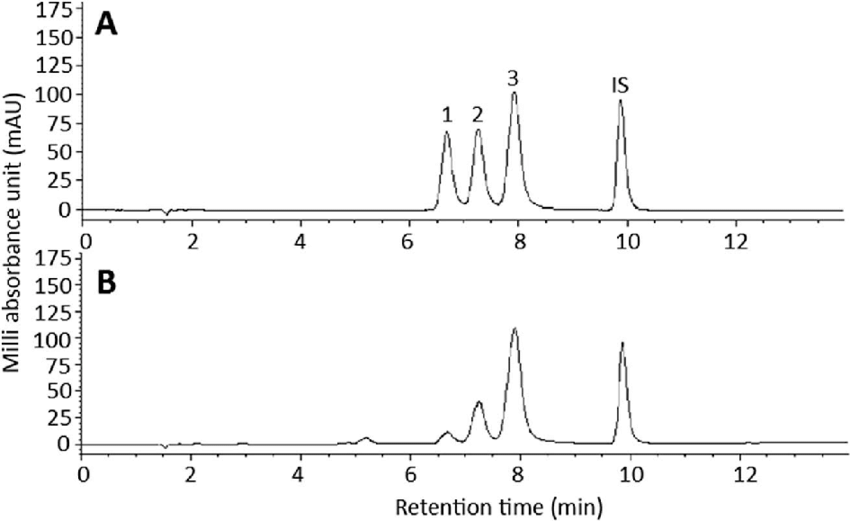
Example of Curcuminoid Analysis Using HPLC
From the chromatogram, it shows the analysis of curcuminoids compared to the standard substance.
Peak 1 corresponds to bisdemethoxycurcumin (BDMC);
Peak 2 corresponds to demethoxycurcumin (DMC);
Peak 3 corresponds to curcumin
Literature:
- N. Maithili Karpaga Selvi, M. G. Sridhar,corresponding author R. P. Swaminathan, and R. Sripradha. “Efficacy of Turmeric as Adjuvant Therapy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients” Indian J Clin Biochem. 2015 Apr; 30(2): 180–186. Published online 2014 May 8. doi: 10.1007/s12291-014-0436-2
- Xhuxhiwin Kanchanathawornviboon1, Chaowalit Monton2 and Hathairat Urairong*1 “Curcuminoids Content of Turmeric Rhizomes Cultivated under Organic Agriculture System in Lop Buri Province” เอกสารสืบเนื่องจากการประชุมวิชาการระดับชาติ มหาวิทยาลัยรังสิต ประจําปี 2564 เผยแพร่ออนไลน์: ลิขสิทธิ © 2559-2564 มหาวิทยาลัยรังสิต
- Sudarat Onsurathum 1, Thidarut Boonmars 2, Somchai Pinlaor 3. “Effect of Curcumin on Opisthorchiasis and Cholangiocarcinoma in Animal Models” (โครงสร้างทางเคมีแสดงในรูปที่ 2) ภาควิชาปรสิตวิทยา, 2 ศูนย์วิจัยพยาธิใบไม้ตับและโรคมะเร็งท่อน้ำดี คณะแพทยศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยขอนแก่น ไชยนิวัตร เลิศกิติยศ “The development of turmeric ( Curcuma longa L.) extract loaded microe mulsions” โครงงานวิจัยทางเภสัชศาสตร์ปีการศึกษา 2563 คณะเภสัชศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยบูรพา
- ภญ.ปิติกาญจน์ กาญจนาพฤกษ์ และ ภญ.ปัณรส แช่มชมดาว.”การผลิตสารมาตรฐานกรมวิทยาศาสตร์การแพทย์ Curcumin สารสำคัญในขมิ้นชัน และการนำสารมาตรฐานไปใช้ในการควบคุมคุณภาพผลิตภัณฑ์” กรมวิทยาศาสตร์การแพทย์
- ขมิ้นชัน สมุนไพรไทยแท้ๆ พร้อมประโยชน์ และการนำไปใช้ให้ถูกวิธี; กันยายน 6, 2018; http://203.157.123.7/ssopanom /?news=สมุนไพร เรื่องน่ารู้ สรรพคุณขมิ้นชัน และประโยชน์มากมาย ที่มากกว่าแค่ใช้ทำอาหาร https://www.sgethai.com/article/สรรพคุณขมิ้นชัน-ขมิ้นชั/#การใช้ประโยชน์จาก_ขมิ้นชัน
- Yen Chu Chen and Bing Huei Chen, 2018, Preparation of curcuminoid microemulsions from Curcuma longa L. to enhance inhibition effects on growth of colon cancer cells HT-29, RSC Advances 8(5):2323-2337.