Service Information: Biomarker Quantification of Rosmarinic Acid using HPLC Technology
VISBIO Limited offers testing and analysis services for biomarker content, specifically of Rosmarinic Acid within the health and beauty products. The significant compounds found in Coleus Amboinicus Lour Leaf, commonly known as Nangsue Samun Phrai Suan Sirirukkhachat include Phenolics, Isoprenoids, Flavone glycosides, and Diterpenoid quinones. Research studies have revealed that the bioactive compounds in these leaves possess anti-inflammatory, antifungal, antibacterial, antioxidant, and anticancer properties. For example, Rosmarinic Acid, a vital bioactive compound in these leaves, exhibits various pharmacological effects, such as antioxidant, antiviral, antibacterial, anti-proliferative, anti-inflammatory properties. It helps alleviate symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, allergic dermatitis, asthma, allergic rhinitis, and importantly, it has anticancer properties particularly in breast cancer.
What is Coleus Amboinicus Lour Leaf or Thai Oregano?
Coleus Amboinicus Lour Leaf, also known as Bai Hue Suea originates from Kenya, Africa, India, Asia, and Australia. It is considered an ornamental plant, a kitchen herb, and a traditional herbal remedy.
The plant is known by different names in various local languages, such as “Niyom Hue Suea” or “Hue Suea” in central Thailand, “Hom Duan Luang” or “Hom Duan Hue Suea” in the northern region. The name “Hue Suea” translates to “tiger’s ear” and is attributed to the plant’s appearance. Coleus Amboinicus Lour Leaf has a fragrance similar to oregano. In the northeastern region of Thailand, it is commonly used by adding young leaves of Coleus Amboinicus Lour to dishes like Menou Lab or foods with strong odors because the plant’s scent helps mask the strong smell of the food.
Key Compounds in Coleus Amboinicus Lour Leaf
Based on past research studies, the bioactive compounds in Coleus Amboinicus Lour Leaf presented anti-inflammatory, antifungal, antibacterial, antioxidant, and anticancer properties. Notable bioactive compounds found in Coleus Amboinicus Lour Leaf extracts include:
- Phenolic compounds like Rosmarinic Acid, Salvianolic acids A and L, Shimobashiric acid C, and various types of methoxylated flavonoids.
- Isoprenoids such as phytosterols and various essential oils.
- Flavone glycosides and diterpenoid quinones, including Royleanone.
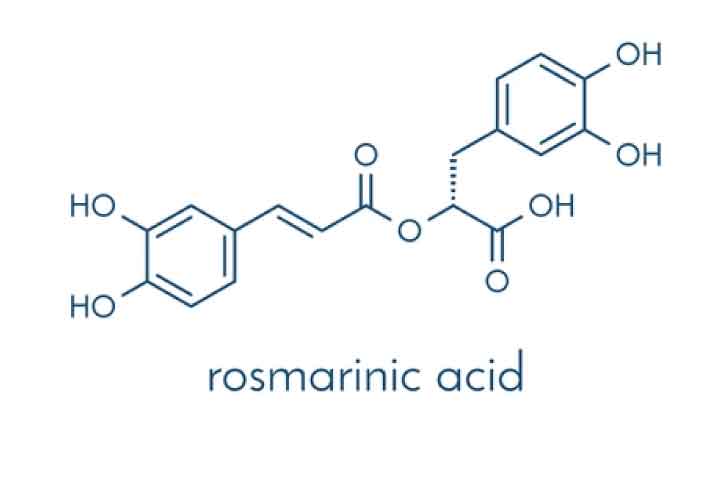
What is Rosmarinic Acid?
Rosmarinic acid is a crucial bioactive component found in extracts from Coleus Amboinicus Lour Leaf. It has a molecular formula of C18H16O8 and belongs to the phenolic group of compounds that are water-soluble. Numerous research studies have revealed diverse pharmacological properties of Rosmarinic acid, such as its antioxidant, antiviral, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory effects. It also inhibits cell death, suppresses tumor growth, and has properties that can alleviate allergic skin reactions, asthma symptoms triggered by allergies, and various inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, colitis, and liver inflammation. These anti-inflammatory effects involve mechanisms such as reducing the production of inflammatory mediators and inhibiting the expression of NF-κB and TNF-α.
Furthermore, research has shown that changes in weather conditions can influence the levels of important substances in Coleus Amboinicus Lour Leaf, such as Rosmarinic acid and various Polyphenols, potentially increasing their concentrations during seasons with intense sunlight, like hot summers.
Extracts from Coleus Amboinicus Lour Leaf in the Herbal and Pharmaceutical Industry:
Coleus Amboinicus Lour Leaf, commonly known as Bai Niyom Hue Suea or Bai Hue Suea is a popular herbal plant widely used for the development of various herbal and pharmaceutical products. It is valued for its diverse pharmacological properties, making it a versatile ingredient.
These properties include aiding digestion, promoting appetite, alleviating coughs, sore throats, antioxidant effects, antiviral and antibacterial properties, anti-inflammatory effects, inhibition of cell death, and anticancer properties. Additionally, it can be used as an external remedy, such as in headache relief (herbal poultice), pain reduction, fever reduction, and swelling alleviation.
Report Example: The Analysis Results of Rosmarinic Acid Using HPLC Technique
Reporting the results of Rosmarinic acid analysis using HPLC technique.
Graph shows the chromatogram of Rosmarinic acid, which allows calculating the quantity of Rosmarinic acid by comparing it with the standard substance based on the area under the curve.
Literature:
- ฐานข้อมูลสมุนไพร คณะเภสัชศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยอุบลราชธานี. “หูเสือ”. [ออนไลน์]. เข้าถึงได้จาก : www.phargarden.com. [23 ก.ย. 2014].
- กรุงเทพธุรกิจ. “หูเสือ แก้ไอ บำรุงเลือด”. [ออนไลน์]. เข้าถึงได้จาก : www.bangkokbiznews.com. [23 ก.ย. 2014].
- หน่วยบริการฐานข้อมูลสมุนไพร สำนักงานข้อมูลสมุนไพร คณะเภสัชศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล. “ใบหูเสือ”. [ออนไลน์]. เข้าถึงได้จาก : www.medplant.mahidol.ac.th. [23 ก.ย. 2014].
- Kaliappan N., Viswanathan P., Pharmacognostical studies on the leaves of Plectranthus amboinicus (Lour.) Spreng. Int. J. Green Pharm. 2008, 2, 182.
- Liu, J., Wan, Y., Zhao, Z. et al. Determination of the content of rosmarinic acid by HPLC and analytical comparison of volatile constituents by GC-MS in different parts of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. Chemistry Central Journal 7, 61 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-153X-7-61
- de Medeiros Gomes, J.; Cahino Terto, M.V.; Golzio do Santos, S.; Sobral da Silva, M.; Fechine Tavares, J. Seasonal Variations of Polyphenols Content, Sun Protection Factor and Antioxidant Activity of Two Lamiaceae Species. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 110. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo C, Zou L, Sun H, Peng J, Gao C, Bao L, Ji R, Jin Y, Sun S. A Review of the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Rosmarinic Acid on Inflammatory Diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2020 Feb 28;11:153. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00153. PMID: 32184728; PMCID: PMC7059186.