Information about the testing service for the quantity of Vitamin C in herbs or products using HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) technique.
VISBIO Co., Ltd. provides testing and analysis services for the quantity of L-Ascorbic Acid or Vitamin C, in various products of the health and beauty industry, as well as the food and beverage industry. Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a water-soluble vitamin that is crucial for health. The human body cannot produce vitamin C on its own due to the lack of the L-gulonolactone oxidase enzyme, so it must be obtained through dietary intake or dietary supplements.
In general, vitamin C is easily degraded when exposed to heat, sunlight and air. Vitamin C is commonly found in sour fruits such as oranges, lemons, cherries or kiwis, as well as in certain vegetables like bell peppers, broccoli, tomatoes. Currently, vitamin C is a popular ingredient in health and beauty products due to its beneficial effects on both health and skin, promoting a healthy complexion and skin radiance.
What is Vitamin C?
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, has a chemical formula of C6H8O6. It is a water-soluble vitamin that is essential for health. The human body cannot produce vitamin C on its own due to the lack of the L-gulonolactone oxidase enzyme, so it must be obtained through dietary intake or dietary supplements. In general, vitamin C is easily degraded when exposed to heat, sunlight and air. Therefore, if fruits and vegetables are stored for a long time, the amount of vitamin C in them will rapidly decrease. Additionally, vitamin C cannot be stored in the body for an extended period, so it is necessary to consume vitamin C daily to meet the body’s needs.
Sources of Vitamin C
Vitamin C is abundant in sour fruits such as oranges, lemons, cherries or kiwis, as well as in certain vegetables like bell peppers, broccoli, tomatoes. For individuals who consume limited fruits and vegetables or store them for an extended period, those who are stressed, exposed to pollution, smoke cigarettes or consume alcohol regularly, there may be an inadequate intake of vitamin C. According to data from the Ministry of Public Health, the majority of Thai people do not consume an adequate number of fruits and vegetables, with only 21.2% meeting the recommended intake (more than 5 servings or 400 grams).
The table shows the quantity of Vitamin C in fruits.
Fruit Name | Quantity per Serving Unit | Vitamin C Quantity (milligrams) |
Kimju Guava | ½ fruit | 138 |
Guava | ½ fruit | 234 |
Kaeg-dum Papaya | 7 berries (6x2x1.5 cm) | 79 |
| Holland Papaya | 4 berries (4×4.5×2 cm) | 109 |
| Lychee | 4 fruits | 62 |
| Strawberries | 9 fruits | 112 |
| Rambutan | 4 fruits | 55 |
| Emblica | 8 fruits | 80 |
Benefits of Vitamin C
Vitamin C, commonly used for health maintenance, offers numerous benefits to the body, including:
- A role in the antioxidant process.
- Protecting cells from free radicals.
- Strengthening blood vessels.
- Aiding collagen production for healthy bones, teeth, gums and skin.
- Providing energy through normal metabolism.
- Supporting the proper functioning of the nervous system.
- Maintaining a well-functioning immune system.
- Helping regenerate vitamin E.
- Enhancing iron absorption.
Vitamin C Requirements for the body
The body’s vitamin C requirements vary based on sex and age:
- Men: 100 milligrams per day.
- Women: 85 milligrams per day.
- Pregnant women: 95 milligrams per day.
- Breastfeeding women: 145 milligrams per day.
- Smokers: An additional 35 milligrams per day.
- Surgical patients may require 200-500 milligrams per day
If the body doesn’t receive an adequate amount of vitamin C, it can lead to a condition called scurvy. Symptoms of scurvy typically occur after not receiving enough vitamin C for 2 months. These symptoms include the development of skin rashes, dry and cracked skin, bleeding gums, swollen and red gums, easy bruising, muscle weakness and fatigue, joint swelling, swollen feet, inflamed nerve endings, slow-healing wounds and hair loss.
Maximum Allowable Vitamin C Intake per Day
Since vitamin C is water-soluble and excreted in urine, excessive intake of vitamin C can lead to side effects such as diarrhea.
The maximum allowable intake of vitamin C without causing side effects is 2,000 milligrams per day. However, there is no clear data on whether high vitamin C intake increases the risk of kidney stones. Nevertheless, individuals at risk of kidney stones should not consume more than 1,000 milligrams of vitamin C per day. Furthermore, individuals at risk of iron overload, such as those with thalassemia, should avoid high-dose vitamin C supplementation as excess iron can accumulate in tissues and lead to tissue damage.
Use of Vitamin C in the Cosmetics Industry
Vitamin C is commonly used in cosmetics and skincare products due to its antioxidant properties. It helps protect cells from free radicals and promotes the production of collagen and whitening. Products containing vitamin C should be packaged in dark or opaque containers to protect them from light, and the containers should be tightly sealed to prevent air from entering, as vitamin C is sensitive to light and air.
Use of Vitamin C in the Food and Dietary Supplement Industry
Vitamin C is a common ingredient in functional drinks, dietary supplements and pharmaceutical products. The Thai Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has set a maximum allowable limit for water-soluble vitamins at 200% of the Thai Recommended Dietary Intake (Thai RDI) for individuals aged 6 and older.
For vitamin C, this limit is 120 milligrams per day. The labeled amount of vitamin C on the product must be accurate, and the product must maintain the labeled amount throughout its shelf life.
Additionally, vitamin C is commonly consumed in the form of dietary supplements and medicines, available in various forms such as tablets, capsules, powders, effervescent tablets, and liquid formulations. These supplements are used to prevent vitamin C deficiency and support skin and overall health. Products containing not up to 60 milligrams of vitamin C per daily serving can be registered as dietary supplements, while products containing more than 60 milligrams per daily serving must be registered as vitamin C medicines, available in injectable or medicines.
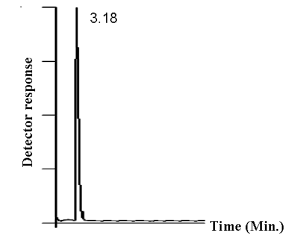
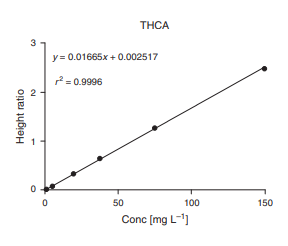
Example of Reporting Vitamin C Analysis Using HPLC Technique
Figure 1
Figure 2
Vitamin C Analysis Using HPLC Technique
Figure 1 shows the chromatogram of Vitamin C, which can be used to calculate the quantity of Vitamin C by comparing it with the standard substance. Figure 2 represents the calculated quantity of Vitamin C.
Literature:
- รายงานการสำรวจสุขภาพประชาชนไทยโดยการตรวจร่างกาย ครั้งที่ 6 พ.ศ.2562-2563, กันยายน 2564.
- ประกาศสำนักงานคณะกรรมการอาหารและยา เรื่อง การแสดงข้อความกล่าวอ้างหน้าที่ของสารอาหาร, เล่ม 136, 10 มิถุนายน 2562.
- ปริมาณสารอาหารอ้างอิงที่ควรได้รับประจำวันสำหรับคนไทย พ.ศ.2563 โดย คณะกรรมการและคณะทำงานปรับปรุงข้อกำหนดสารอาหารที่ควรได้รับประจำวันสำหรับคนไทย สำนักโภชนาการ กรมอนามัย กระทรวงสาธารณสุข.
- คุณค่าทางโภชนาการในผลไม้, กรมอนามัย กระทรวงสาธารณสุข, 2553.
- ประกาศสํานักงานคณะกรรมการอาหารและยา เรื่อง ข้อกําหนดการใช้ส่วนประกอบที่สำคัญของผลิตภัณฑ์เสริมอาหารชนิดวิตามินและแร่ธาตุ, 2549.
- Mohamed H.S. Ahmida, Determination of Ascorbic Acid in Vitamin C (Tablets) by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography, Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 8 (2009), 6463-6467