Information about the service for testing the efficiency of LDL (Low-Density Lipoproteins) cholesterol production.
VISBIO Co., Ltd. offers a service to analyze the production quantity of LDL (Low-Density Lipoproteins) cholesterol and determine the appropriate concentration of products in the health and beauty industry to prevent excessive LDL cholesterol production. This analysis is conducted using the ELISA method.
Cholesterol is a type of fat found in the cell membranes of all human cells, and it can be divided into 2 types: LDL Cholesterol, which is harmful, and HDL Cholesterol, which is beneficial. Testing the production of LDL cholesterol can be performed by analyzing various samples such as herbs, ingredients, raw materials, extracts, dietary supplements, herbal products, or medicines using the Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) or Enzyme Immunoassay (EIA) methods. These tests are based on immunology principles and involve specific reactions between antigens and antibodies.
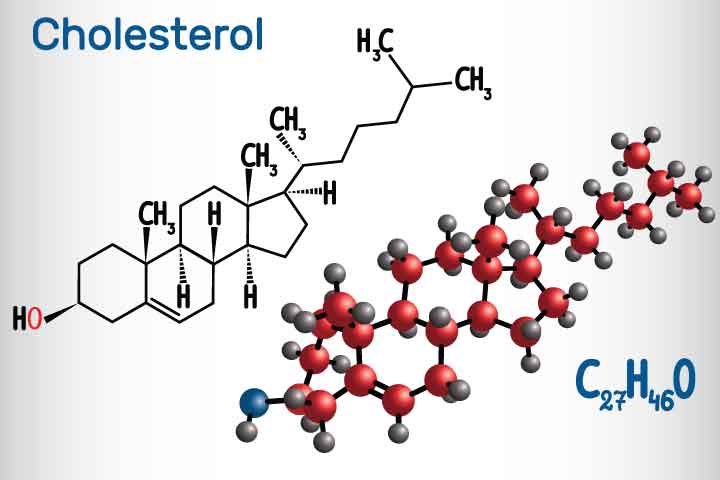
What is Cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a type of fat found in the cell membranes of every cell in our bodies and is also a component of bile. Our bodies obtain cholesterol from the food we eat, especially from animal products rich in fatty acids. Additionally, our liver can synthesize cholesterol on its own. When the intake of cholesterol from our diet exceeds the body’s needs, it can accumulate in our system.
Cholesterol can be divided into 2 types:
- LDL Cholesterol, which stands for Low-Density Lipoproteins, is considered “bad cholesterol” because it adheres to the walls of red blood vessels, leading to reduced flexibility and the development of narrowed blood vessels.
- HDL Cholesterol, which stands for High-Density Lipoproteins, is beneficial because it prevents LDL from adhering to the walls of red blood vessels, thus helping to prevent the development of narrowed blood vessels.
Testing cholesterol levels can help identify the risk of fat accumulation in blood vessels and related diseases. However, high cholesterol levels may not always show symptoms. The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) recommends that individuals aged 9-11 have their cholesterol levels checked for the first time, followed by retesting every 5 years. For individuals aged 45-65, both men and women, cholesterol testing should be performed every 1-2 years. Cholesterol testing (LDL) can be done through blood tests, including calculating the four types of fats in the blood:
- Total cholesterol, which is the sum of cholesterol in the blood.
- Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol.
- High-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol.
- Triglycerides, which is one type of fat in the blood. When excess calories are consumed from food, the body converts them into triglycerides and stores them in cells.
Cholesterol levels (LDL)
| LDL (Bad) Cholesterol Level | LDL Cholesterol Category |
|---|---|
| Less than 100mg/dL | Optimal |
| 100-129mg/dL | Near optimal/above optimal |
| 130-159 mg/dL | Borderline high |
| 160-189 mg/dL | High |
| 190 mg/dL and above | Very High |
Factors Affecting LDL Cholesterol Levels in the Body
- Diet: Consuming a diet high in saturated fats, such as red meat, fatty cuts of meat, and animal fats, in excessive quantities can lead to the accumulation of LDL cholesterol.
- Physical Activity: Regular physical activity, at least 150 minutes per week, can help reduce LDL cholesterol levels.
- Smoking/Alcohol Consumption: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to elevated LDL cholesterol levels.
- Age and Gender: Age and gender can play a role in LDL cholesterol levels, with levels tending to increase with age. Additionally, gender differences may influence cholesterol levels.
- Genetics: Genetic factors can predispose individuals to higher or lower LDL cholesterol levels.
- Medications: Some medications, including certain steroids, can increase LDL cholesterol levels. It is essential to take these medications as prescribed by a healthcare provider.
Using the ELISA Method for Measuring Cholesterol Levels
There are several methods available to measure cholesterol levels in the body or in food, and one of the specific techniques is Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) or Enzyme Immunoassay (EIA). ELISA is a testing method that relies on the principles of immunology and involves specific interactions between antigens and antibodies.
The basic principle of the ELISA method involves coating an ELISA plate’s surface with an antigen or antibody, which is labeled with an enzyme. Then, when a substrate solution is added, it reacts with the enzyme and changes color. Subsequently, the color change is measured by reading the absorbance of light using a Microplate Reader. ELISA can be used for both quantitative and qualitative assessments.
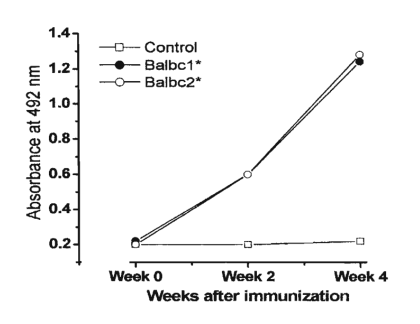
Example: Research on the Production of Monoclonal Antibodies for Measuring Cholesterol Levels in Japanese Quail Egg Using the ELISA Method, creating a Graph Based on the Light Absorbance Values of Immune Response Each Week
From the graph, it shows the chromatogram of vitamin B12 present in the fortified cereal. This allows for the calculation of the quantity of vitamin B12 by comparing it with the standard substance.
Literature:
- ปิยมาส ตัณฑ์เจิรญรัตน์ และ เพทาย พงษ์เพียจันทร์, “การผลิตโมโนโคลนอลแอนติบอดีเพื่อวัดปริมาณโคเลสเตอรอลในไข่แดงของนกกระทาญี่ปุ่น”, วารสารเกษตร 18(3) (2545) : 270-280
- ค้นวันที่ 15 ธันวาคม 2565 จาก https://medlineplus.gov/ldlthebadcholesterol.html
- ค้นวันที่ 15 ธันวาคม 2565 จาก https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/cholesterol-test/about/pac-20384601
- ณัฐธนัญ ภิญโญสุขี, รัตนาวดี วิชาจารณ์และนุชนาฎ ชัชวาลการพาณิชย์, การพัฒนาวิธี ELISA สำหรับตรวจหาปริมาณแอนติบอดีต่อไกลโคโปรตีนดีของไวรัสเฮอร์ปีส์. สถาบันชีววิทยาศาสตร์ทางการแพทย์ กรมวิทยาศาสตร์การแพทย์