Service Information: Testing the Efficacy of Sirtuin Gene Activation through PCR
VISBIO Co., Ltd. offers efficiency testing service of Sirtuin gene expression using PCR in a laboratory setting. This service is conducted by scientific experts and involves cell culture under 2D cell culture conditions. It is available for a wide range of products in the health and beauty industry. Sirtuin genes are a group of genes that encode proteins, specifically enzymes related to various biological processes such as nutrient metabolism, cell growth, and DNA repair. Sirtuin genes have gained significant attention due to their potential in promoting longevity and preventing age-related diseases like cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, and heart disease. The efficiency of sirtuin gene expression can be analyzed in a laboratory setting under 2D cell culture conditions for various raw materials, ingredients, herbs, pharmaceutical products, herbal products, and dietary supplements.
Get to Know Sirtuin Genes
“Sirtuin” genes, also known as the Sirtuin gene, belong to a group of genes associated with promoting longevity. There are seven different types of Sirtuin genes in humans, known as SIRT1 to SIRT7. These genes play a critical role in controlling biological processes and cellular pathways associated with aging and extended longevity. The functionality of Sirtuin genes can be influenced by external factors such as lifestyle, diet, exercise, and stress.
Each type of Sirtuin gene is located in different cellular components and performs various functions, including:
- SIRT1 gene, found in the nucleus and cytoplasm, helps regulate metabolism, stress responses, and cell survival.
- SIRT2 gene, located in the cytoplasm, controls the cell division cycle and cell growth.
- SIRT3 gene, residing in the mitochondria, responsible for maintaining metabolic balance, combating oxidative stress, and regulating cellular energy consumption.
- SIRT4 gene, also in the mitochondria, controls insulin secretion and fatty acid oxidation.
- SIRT5 gene, situated in the mitochondria, involves in the regulation of urea cycle and ammonia detoxification.
- SIRT6 gene, present in the nucleus, helps maintain metabolic balance, DNA repair, and anti-inflammatory responses.
- SIRT7 gene, found in the mitochondria, responsible for decoding genetic information.
Analysis of Sirtuin gene production using PCR techniques
The research is centered around creating different types of Sirtuin genes crucial for regulating processes linked to aging and longevity. This involves studying the rejuvenating effects of extracts, understanding how cells survive in culture, and examining how cancer cells perish. The widely employed 2D cell culture method enables the cultivation of cells or tissues taken directly from living organisms in a controlled external setting. This approach facilitates the adjustment of conditions to stimulate swift cell growth, multiplication, and the expression of distinct cell features. Cells cultured using this method closely imitate those present in experimental animals or the human body. It possesses various properties similar to cells transplanted into laboratory animals or cells within the body. Before being analyzed for sirtuin gene expression using Real-time PCR (RT-PCR), which is a technique amplifying the amount of DNA required for study and allowing measurement of the DNA quantity in each reaction round instantly.
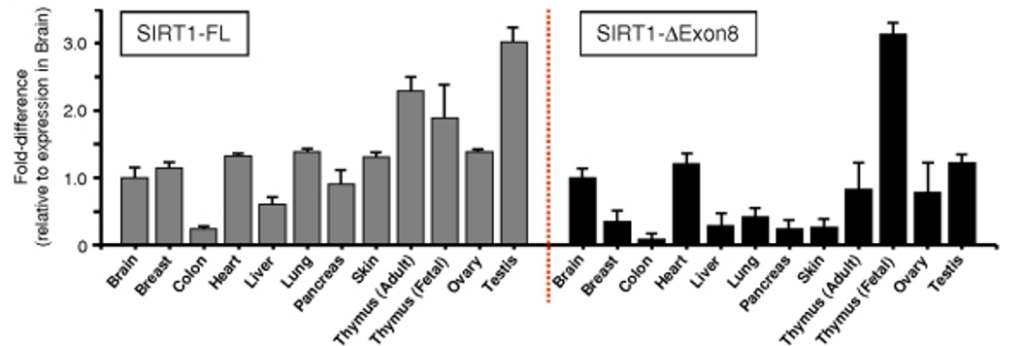
Report Example: Sirtuin Gene Expression Analysis Report Using PCR Technique
The figure illustrates the expression of SIRT1-FL and SIRT1-ΔExon8 genes in various human organ tissues using the RT-PCR technique, related to the expression levels in the brain
Literature:
- บัณฑรวรณ ธุระพระและคณะ, การประเมินอายุชีวภาพด้วยความยาวเทโลเมียร์, การประชุมวิชาการเสนอผลงานวิจัยระดับบัณฑิตศึกษาแห่งชาติ ครั้งที่ 21, วันที่ 27 มีนาคม 2563.
- ณฉัตรีย์ วุฒิพันธุ์ชัย, การจำกัดพลังงานที่ได้รับจากอาหารเพื่อการมีอายุขัยที่ยืนยาว, ปริญญาวิทยาศาสตร์มหาบัณฑิต สาขาวิชาวิทยาการชะลอวัยและฟื้นฟูสุขภาพ วิทยาลัยการแพทย์บูรณาการ มหาวิทยาลัยธุรกิจบัณฑิตย์, 2561.
- Gaebler M, Silvestri A, Haybaeck J, Reichardt P, Lowery CD, Stancato LF, et al. Three-dimensional patient-derived In vitro sarcoma models: promising tools for improving clinical tumor management. Front Oncol 2017; 7: 203.
- Lynch, Cian & Shah, Zahid & Allison, Simon & Ahmed, Shafiq & Ford, Jack & Warnock, Lorna & Serrano, Manuel & Milner, Jo. (2010). SIRT1 Undergoes Alternative Splicing in a Novel Auto-Regulatory Loop with p53. PloS one. 5. e13502. 10.1371/journal.pone.0013502.