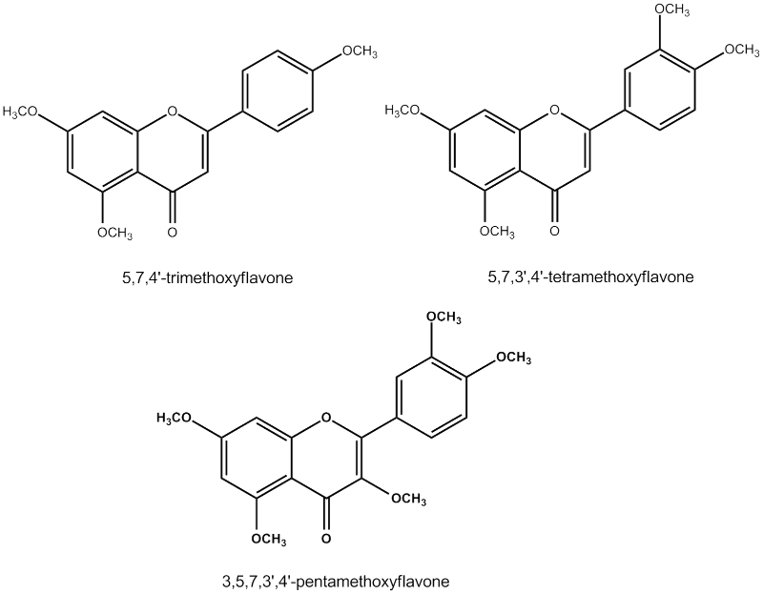
Service Information for Testing the Quantity of 5,7,4’-Trimethoxyflavone or 3,5,7,3,4 Pentamethoxyflavone using HPLC
VISBIO offers services for the examination and analysis of the quantity of biomarker components such as 5,7,4’-trimethoxyflavone or 3,5,7,3′,4′-pentamethoxyflavone in all products within the health and beauty industry. These substances are significant components found in black ginger, which is considered to be of equivalent quality to Korean ginseng. It is even referred to as “Thai ginseng” and is known for its potential to enhance sexual potency, act as a rejuvenating agent, and slow down aging. Black ginger consists of various components including essential oils, flavonoids, and flavones such as –
dimethoxyflavone, -trimethoxyflavone, -tetramethoxyflavone, and 3,5,7,3′,4’-pentamethoxyflavone, as well as anthocyanins and phenolic compounds.
Currently, there are three popularly extracted important compounds from black ginger for beneficial use, namely: 5,7-Dimethoxyflavone, 5,7,4’-Trimethoxyflavone, and 3,3’,4’,5,7-Pentamethoxyflavone. These compounds possess properties that contribute to overall well-being, help regulate blood sugar, slow down aging, and provide benefits in enhancing male sexual potency.
Black Ginger
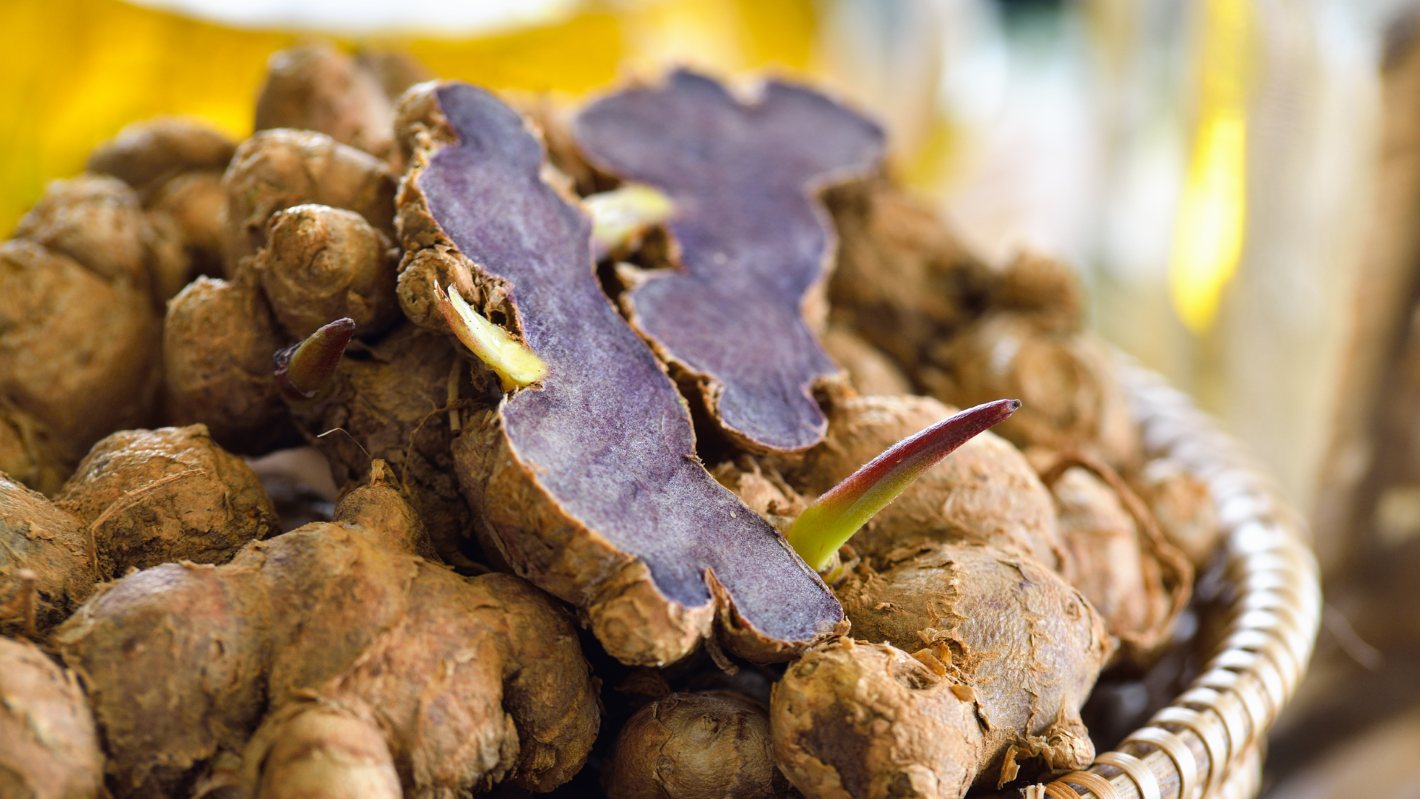
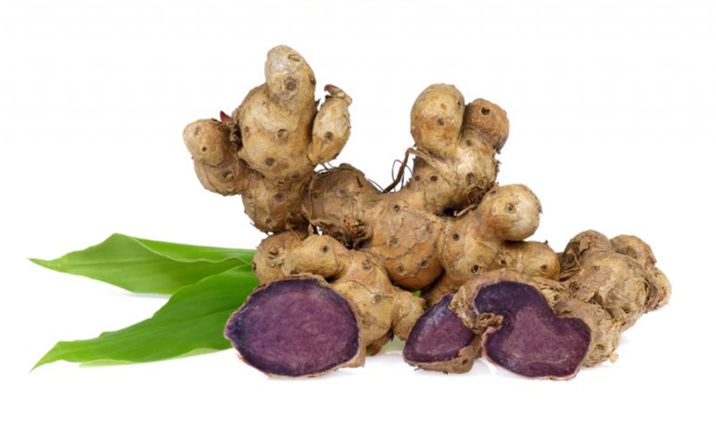
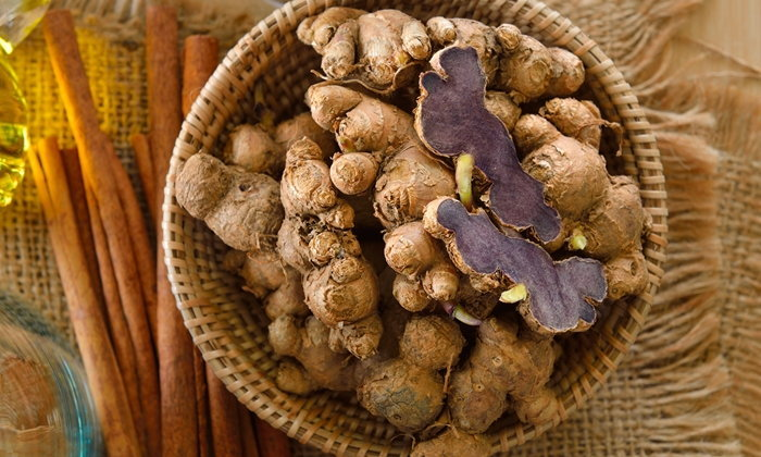
Black Ginger (Kaempferia parviflora Wall. ex Baker) belongs to the same family as galangal, turmeric, ginger, and cardamom (Zingiberaceae). It is a plant native to the hot regions of Southeast Asia, particularly found in the southern and eastern parts of Thailand, often growing naturally in mountainous areas. It has a scientific name, Kaempferia parviflora Wall. ex Baker, and is commonly known as “black ginger” due to its appearance. The rhizomes of black ginger resemble ginger, but the inner flesh is dark purple.
Black Ginger is cultivated throughout various regions of Thailand, with a significant portion being grown in the northern part of the country. The different varieties of Black Ginger can be categorized based on the color of their inner flesh. They are grouped into those with dark purple to almost black flesh and those with lighter purple or pale-colored flesh. The color of the inner flesh is believed to indicate the quality of the Black Ginger. In trade, Black Ginger with darker purple flesh is often considered of higher quality, while those with lighter purple flesh are considered of lower quality and might be categorized as a different type of ginger.
- Black turmeric has a round shape with its skin ranging from light brown to dark brown. Sometimes, there might be marks on the skin around the area where new shoots will sprout. The interior of the tuber comes in shades of light purple, deep purple, and even black. The tuber emits a distinct aroma and has a slightly bitter taste.
- The leaves of black turmeric are solitary, resembling an oval or egg shape with pointed tips and serrated edges along the leaf veins. The surface of the leaves features wavy ridges along the leaf veins. The leaves are a vibrant green color.
- Black turmeric flowers appear in clusters emerging from the base of the leaf sheath. The male flowers have a white color and a parallel-edged shape. The petal lobes are purple.
Important Components and Chemical Structure of Black Ginger
Black ginger rhizomes consist of various compounds including essential oils, flavonoids, anthocyanins, and other phenolic compounds. The major constituents include aromatic essential oils, flavonoids (specifically flavones such as -dimethoxyflavone, -trimethoxyflavone, -tetramethoxyflavone, and 3,5,7,3′,4′-pentamethoxyflavone), anthocyanins, and other phenolic compounds. Generally, the rhizomes with darker flesh have higher amounts of phenolic compounds and flavonoids compared to those with lighter-colored flesh. Rhizomes with lighter flesh contain higher levels of aromatic essential oils compared to those with green coloration.
Currently, three types of important compounds extracted from black ginger rhizomes for various applications are recognized: 5,7-Dimethoxyflavone, 5,7,4′-Trimethoxyflavone, and 3,3′,4′,5,7Pentamethoxyflavone.
Pharmacological Studies
- 5,7-Dimethoxyflavone (5,7-DMF), a compound extracted from black ginger rhizomes, possesses antiinflammatory properties and fever-reducing effects.
- Compounds like 5,7,4′-trimethoxyflavone and 5,7,3′,4′-tetramethoxyflavone exhibit anti-Plasmodium falciparum activity, which is responsible for causing malaria. Additionally, compounds like 3,5,7,4’tetramethoxyflavone and 5,7,4′-trimethoxyflavone demonstrate anti-Candida albicans and antiMycobacterium properties.
- Reproductive System EffectsBlack ginger extracts have been found to enhance blood circulation to sexual organs (based on animal experiments) and research reports suggest an increase in the density of Leydig cells.
Thai Traditional Medicine and Health Benefits of Black Ginger for the Body
In Thai traditional medicine, black ginger is found to have various uses and benefits, as follows:
- Used as an anti-aging remedy to delay the effects of aging. It holds valuable traditional properties by slicing the rhizome into thin pieces, sun-drying them until they are dry, then grinding them into a fine powder. This powder is mixed with honey to create a “luuk klon” (candy-like preparation).
- Utilized as a tonic to strengthen the body. The rhizome is combined with other herbs to create an alcohol-infused tonic.
- Nourishes and revitalizes the complexion of women, providing a radiant and youthful appearance.
- Supports male hormonal balance. If women consume it, it helps regulate sex hormone balance.
- Stimulates the nervous system, nourishes nerves, and enhances overall body strength.
- Aids in improving sleep quality, alleviating insomnia and enhancing overall sleep.
- Enhances blood circulation throughout the body, promoting better blood flow.
In modern times, aside from using black ginger as a fresh or dried herb, it’s also processed into various forms for consumption. These include powdered sachets for making herbal drinks known as “nam kachai dam,” black galangal candies, and most popularly, “black ginger wine.” It’s also made into herbal capsules, powdered preparations, and “black ginger coffee.” Research suggests that black ginger can have positive effects on sexual performance, blood flow to sexual organs, and muscle relaxation, leading to improved sexual function in men. However, it’s important to note that there’s limited research in humans, and there’s insufficient guidance on appropriate dosages and long-term safety when used over an extended period.
What are the products made from black ginger?
Products made from black ginger have a wide variety in the current market. Examples include food and beverages, such as black ginger snacks, black ginger powder, black ginger tea, black ginger wine, and black ginger coffee. There are also beauty products like black ginger soap, black ginger massage oil, black ginger face masks, and black ginger essential oil. In the realm of health products, you can find black ginger extracts, black ginger capsules, black ginger water, and black ginger ointment. Even black ginger adhesive patches are available.
Development of black ginger and health products in the present
Black ginger possesses the potential for becoming a medicinal herb and health supplement due to scientific research confirming its various important biological and pharmacological properties.
Fresh black ginger is produced annually for domestic consumption and is sometimes exported after basic processing such as drying, grinding, or extraction. Approximately 10% of the production is intended for export, while nearly all of it is used in the food and pharmaceutical industries within the country. However, in the cosmetics industry, black ginger is used to a much lesser extent.
Thai black ginger is comparable in quality to Korean ginseng and is believed to have aphrodisiac properties, leading to it being referred to as “Thai Ginseng” or “Natural Viagra”. There has been an increasing number of products derived from black ginger due to market demand, providing income to farmers who cultivate black ginger. Moreover, efforts have been made to enhance the quality of Thai black ginger by increasing its key constituents, resulting in the development of new products for the domestic market and exploring avenues for export.
In the pharmaceutical industry, various products have been developed, including internal medications like black ginger pills, black ginger capsules, black ginger powder pills, and black ginger water solutions. In the food industry, health supplement products have been created to suit consumer needs, such as black ginger wine, black ginger coffee, black ginger tea, and other herbal beverages.
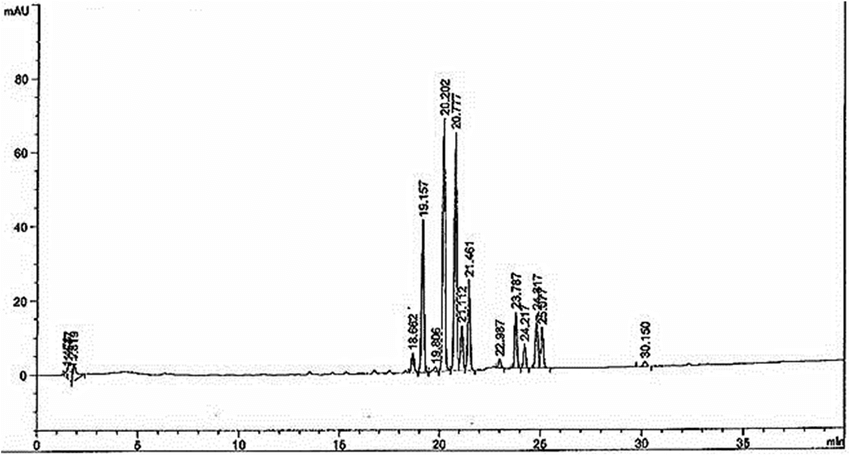
Example of Reporting Results of Black Ginger Extract (Kaempferia parviflora rhizome extract) Using HPLC Instrument
From the graph, it demonstrates the chromatogram of the biological components (Biomarkers) of black ginger extract.
Literature:
- “กระชายดำกับสมรรถภาพทางเพศชาย” อรัญญา ศรีบุศราคัม, สำนักงานข้อมูลสมุนไพร คณะเภสัชศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล
- “ฤทธิ์ 1 เดือนของสารสกัดกระชายดาต่อระดับน้าตาลและระดับไขมันในเลือดของหนูแรท” สมสุดา โสมอินทร์*, ชูวดี ปริวัฒนากุล, บังอร ศรีพานิชกุลชัย, กิตติศักดิ์ ศรีพานิชกุลชัย, ภาควิชากายวิภาคศาสตร์ คณะแพทยศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยขอนแก่น, 24 มกราคม 2561
- “The Development Strategies for Black Galingale and Its Products”, พนารัช ปรีดากรณ์, เติมธรรม สิทธิเลิศ, ผู้ช่วยศาสตราจารย์ ดร. ประจำคณะเศรษฐศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยหอการค้าไทย
- “สารสกัดกระชายดำ” เว็บไซต์: https://www.disthai.com/สารสกัดกระชายดำ สืบค้นเมื่อวันที่ 7 มกราคม 66
- สถาบันวิจัยสมุนไพร กรมวิทยาศาสตร์การแพทย์ กระทรวงสาธารณสุข.(2552). สมุนไพรน่ารู้ (4)กระชายดำ Kaempferia parviflora Wall. ex Baker. กรุงเทพฯ โรงพิมพ์สำนักงานพระพุทธศาสนาแห่งชาติ.
- อรัญญา ศรีบุศราคัม.กระชายดำกับสมรรถภาพทางเพศชาย.บทความเผยแพร่ความรู้สู่ประชาชน.คณะเภสัชศาสตร์มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล.
- “Journal of Thai Traditional & Alternative Medicine” Vol. 11 No. 1 January-April 2013
- “Development of Instant Herbal Beverage from Kaempferia parviflora Wallich. ex Baker” มจ.1-62-01-032 : การพัฒนาการผลิตและการใช้ประโยชน์จากพืชสมุนไพรไทย: กรณีศึกษากระชายดำ
- Waluga Plaingama, Siriporn Sangsuthumb, Wannee Angkhasirisapc,Tewin Tencomnao, 2017, Kaempferia parviflora rhizome extract and Myristica fragrans volatile oil increase the levels of monoamine neurotransmitters and impact the proteomic profiles in the rat hippocampus: Mechanistic insights into their neuroprotective effects, Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine 7(4).