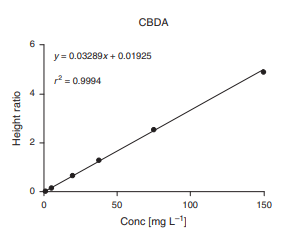
Service Information: Biomarker Quantification Testing for Cannabis Compounds such as CBD, CBDV or CBDA using HPLC
VISBIO Co., Ltd. offers services to analyze and quantify the biomarkers of CBD, CBDV or CBDA in various products within the health and beauty industries or food and beverage industries. Cannabinoids are a crucial group of compounds found in cannabis, and they come in various forms. For example, CBD (Cannabidiol) is a terpenophenolic compound known for its anti-convulsant properties, which can help reduce seizure frequency in patients with epilepsy. It also promotes relaxation, anxiety reduction, sleep improvement, appetite stimulation, nausea relief, pain alleviation, and anti-inflammatory effects. Additionally, it can mitigate the psychoactive effects of THC, making it a popular choice for use in dietary supplements, cosmetics, and food products. CBDV (Cannabidivarin) is another compound that doesn’t affect the nervous system. Research has shown that CBDV can help alleviate symptoms of epilepsy, nausea and vomiting. Lastly, CBDA (Cannabidiolic acid) has anti-inflammatory properties and can help with nausea and anxiety relief. When using cannabis extracts in products, it’s essential to adhere to quality standards. The level of active compounds must be consistent and free from excessive THC content. The products should also be free from contaminants. Quality control measures are in place to ensure that cannabis extracts used in products are safe and effective for various applications.
Getting to Know Cannabis
Cannabis, scientifically known as Cannabis sativa L. subsp. indica (Lam.), has been used as a medicinal remedy in ancient pharmacopeias for thousands of years. Its documented usage dates back to the 8th century in ancient Arabic pharmacopeias and is also found in traditional Chinese, Thai and British pharmacopeias. Cannabis is a robust plant that thrives in warm climates, reaching approximately 2-4 feet in height, with leaves that are palmate, resembling either hemp or marijuana leaves. A single leaf typically contains about 5-7 palmate lobes on a single stem.
Cannabis is permitted for medicinal and recreational use in many countries. It consists of numerous active chemical compounds, with cannabinoids being a major group, primarily found in the female flower’s trichomes. They are usually in the form of carboxylic acid or acid form, but when exposed to light and heat, they decarboxylate into their neutral form. The prominent cannabinoids with pharmacological effects are THC (Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (Cannabidiol).
However, cannabis comprises various cannabinoids and other compounds like flavonoids, steroids, terpenes, fatty acids, and more, and some of them are present in trace amounts, accurately analyzing and quantifying these substances is not a straightforward task. Due to the limitations of current analytical standards, various techniques have been developed for qualitative and quantitative analysis of these substances. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is one of the preferred methods for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of different compounds in cannabis, allowing for the quality control of extracts or herbs.
Cannabis extracts
Cannabis extracts are commonly derived from the female flowers of cannabis plants, which have high concentrations of chemical compounds. The major components are typically cannabinoids, including THC (Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (Cannabidiol). These two substances are fat-soluble and are often extracted using oils.
Each cannabis plant strain has varying levels of THC and CBD in different proportions. These levels depend on environmental conditions and cultivation techniques, leading to variations in the extracted from different sources.
Cannabis extracts come in various forms today, such as oils, resin and have been developed into various products, including cosmetics, food, bakery, beverages, dietary supplements or prescription medications.
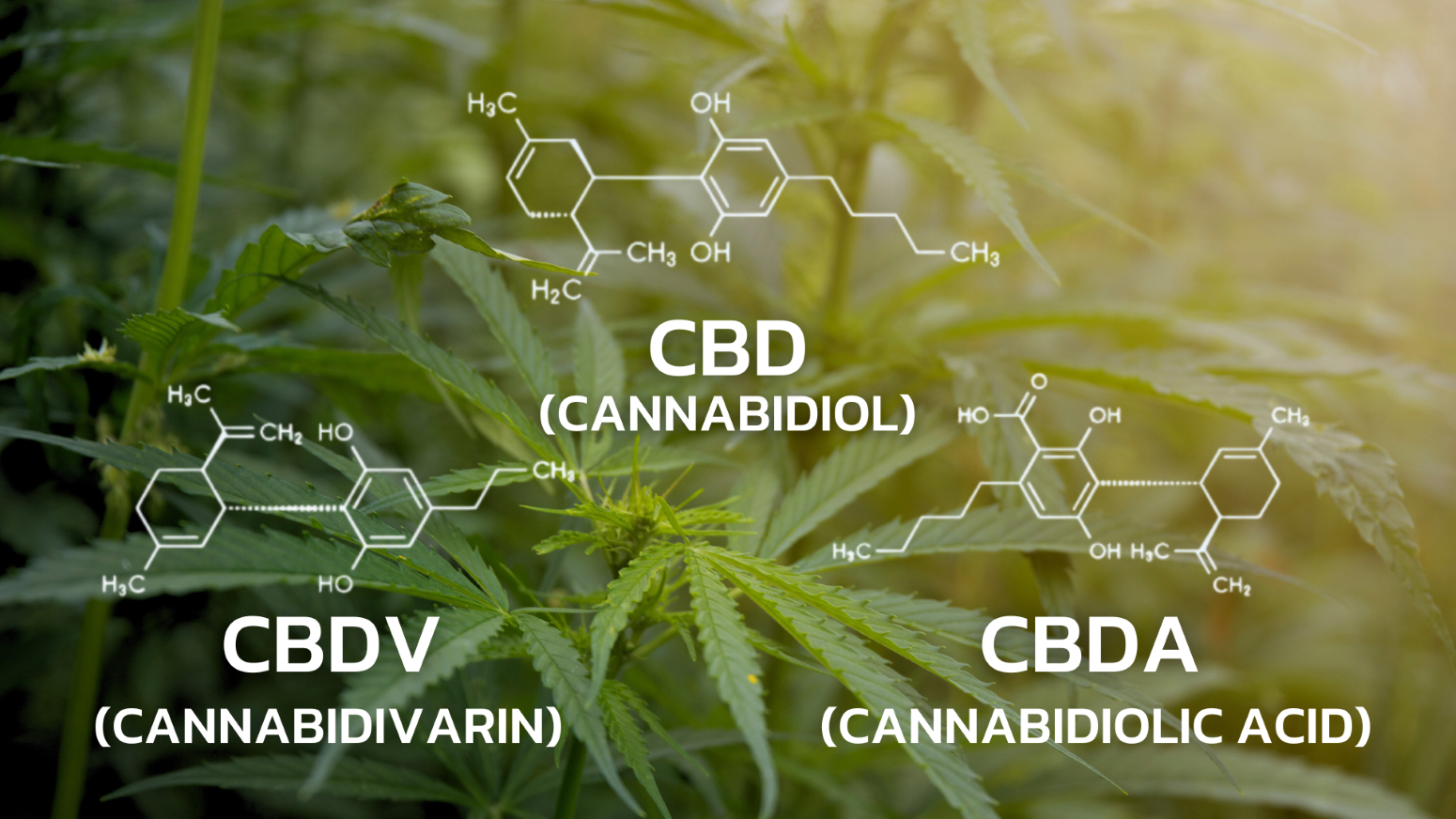
What is CBD, or Cannabidiol?
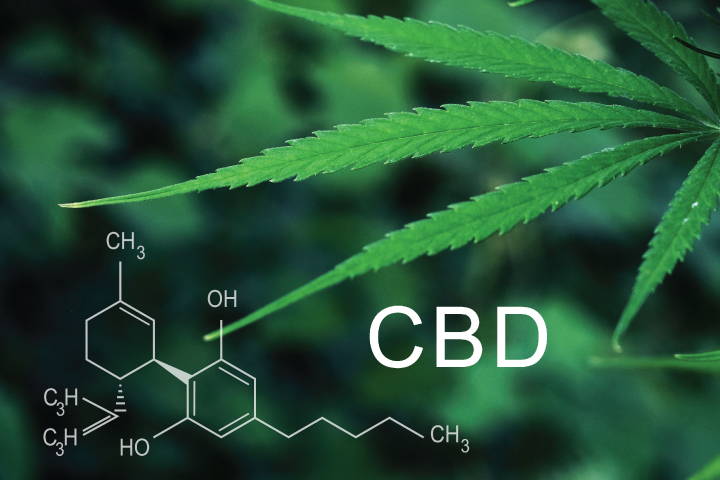
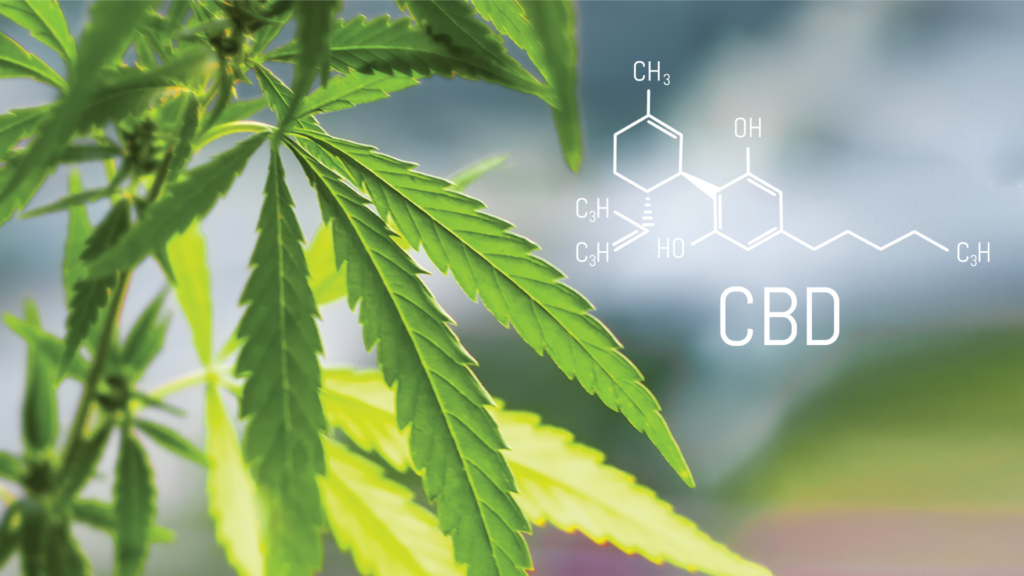
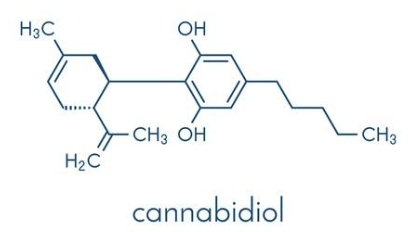
CBD or Cannabidiol, is a naturally occurring molecule with the molecular formula C21H30O2. It is one of the cannabinoids found in cannabis and is typically obtained from the hemp plant. CBD is a white, crystalline powder that is highly soluble in oils. It is a terpenophenolic compound composed of 21 carbon atoms and is derived from the decarboxylation of CBDA (Cannabidiolic acid). CBD can also be synthesized through various processes.
CBD is one of the most extensively researched cannabinoids and is well-known for its widespread use. It is commonly found in over-the-counter dietary supplements and prescription medications. Generally, CBD is considered safe, with no reports of severe toxicity or adverse side effects. Any reported side effects are typically associated with drug interactions between CBD and other medications taken by patients.
CBD does not have psychoactive effects and does not produce a “high.” It is known to have several potential therapeutic benefits, including reducing the frequency of seizures in individuals with epilepsy, promoting relaxation and anxiety reduction, aiding in sleep, supporting appetite, alleviating nausea, relieving pain and reducing the negative side effects of THC, such as intoxication and paranoia.
Figure 1 The structure of CBD.
What is CBDV (Cannabidivarin)?
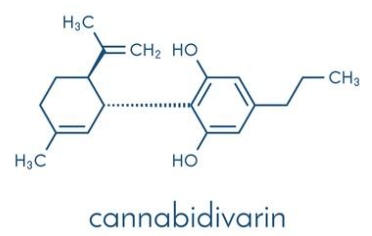
CBDV (Cannabidivarin) has a molecular formula of C19H26O2 and is one of the cannabinoids found in cannabis. CBDV is derived from the conversion of CBCVA (Cannabichromvarinic acid) to CBDVA (Cannabidivarinic acid), and then CBDVA is further decarboxylated to become CBDV (Cannabidivarin). CBDV does not have psychoactive effects and research suggests that it may help alleviate symptoms of epilepsy, nausea and vomiting.
Figure 2 The Structure of CBDV
What is CBDA (Cannabidiolic acid)?
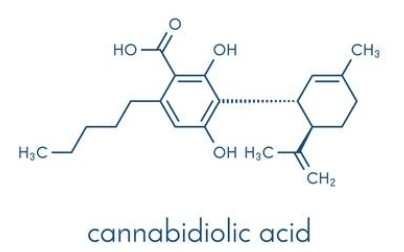
CBDA (Cannabidiolic acid) has a molecular formula of C21H30O2 and is an important compound in the Cannabinoids group found in cannabis. CBDA is derived from the conversion of CBGA (Cannabigerolic acid) into CBDA. CBDA is not very stable because when it is in a dry and hot condition, it breaks down from CBDA to CBD (Cannabidiol).
CBDA has a molecular structure similar to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and there have been numerous research studies showing that CBDA helps with inflammation. Additionally, CBDA is known to relieve nausea and anxiety.
Figure 3 The structure of CBDA (Cannabidiolic acid)
The use of cannabis extracts in the food industry
Cannabis extracts containing CBD are widely used in various food and beverage products such as fruit juices, cocktails, chewing gum, jelly, cookies, brownies, chocolates, and more. These products may contain significantly higher amounts of the substance than naturally found in cannabis. From the outside, these products may not appear different from regular food items, so it is important to control the quantity of chemical compound to ensure consumer safety.
The use of cannabis extracts in the beauty industry
Cannabis extracts containing CBD can be used in beauty and skincare products such as cosmetics, hair care products and skin care products, including creams, bath salts, soap, lip gloss and mascara. CBD has properties that help reduce inflammation, combat free radicals, and moisturize the skin. Additionally, it can also be used in toothpaste and perfumes. However, in Thailand, there are regulations controlling the use of extracts in cosmetics, specifying that the maximum concentration of CBD in finished products should not exceed 1% w/w, and warning labels must comply with the law.
The use of cannabis extracts for medical purposes
Due to the fact that cannabis has various strains, each strain has different proportions of active compounds, resulting in varying therapeutic effects and side effects. Therefore, when using cannabis for medical purposes, it is essential to know the specific type and quantity of active compounds. In Thailand, there has been continuous research and development of medical cannabis products, mainly utilizing THC (Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (Cannabidiol). CBD is known for its pain-relieving and seizure-controlling properties. The most common form of CBD used is sublingual CBD oil, which may contain different ratios of THC and CBD. For instance, products with only THC are used to alleviate nausea and vomiting from chemotherapy, products with only CBD are used in patients with difficult-to-treat or drug-resistant epilepsy, and products with a 1:1 ratio of THC to CBD are used for conditions like muscle stiffness in patients with multiple sclerosis.
Using cannabis extracts for medical purposes requires strict control of the cannabis standards. The products must contain a consistent amount of active compounds without excessive THC levels or contaminants like heavy metals and pesticides. Proper dosing and administration methods must be established, quality and quantity control of the cannabis extracts is crucial to ensure both effectiveness and safety in medical applications.
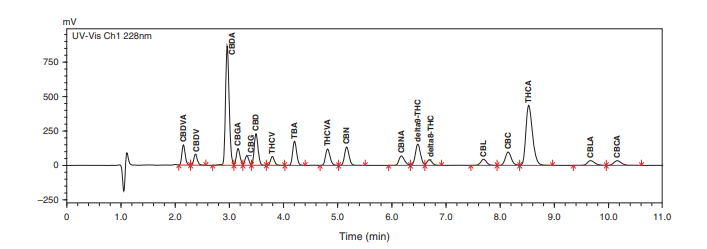
Example of Analyzing 17 Types of Phytocannabinoids in 11 Minutes Using HPLC Technique
Figure 1
Figure 2
From Figure 1, it shows the chromatogram of 17 types of Phytocannabinoids. By integrating the area under the curve, the quantities of the 17 different substances are calculated, compared to the standard substances. An example of Figure 2 displays the quantity of THCA that has been calculated.
Literature:
- กองควบคุมวัตถุเสพติด สำนักงานคณะกรรมการอาหารและยา, ตุลาคม 2563.
- Brenneisen R. “Chemistry and analysis of Phytocannabinoids and Other Cannabis Constituents” in Marijuana and the Cannabinoids. Humana Press, New Jersey, pp. 17-49, 2007.
- Galettis, Peter & Williams, Michelle & Gordon, Rebecca & Martin, Jennifer. (2021). A Simple Isocratic HPLC Method for the Quantitation of 17 Cannabinoids. Australian Journal of Chemistry. 74. 10.1071/CH20380.
- Hanus LO, Meyer SM, Munoz E, Taglialatela-Scafati O, Appendino G. Phytocannabinoids : a unified critical inventory. Nat Prod Rep 2016; 33(12) : 1357-92.
- De Petrocellis L, Ligresti A, Moriello AS, Allarà M, Bisogno T, Petrosino S, Stott CG, Di Marzo V. Effects of cannabinoids and cannabinoid-enriched Cannabis extracts on TRP channels and endocannabinoid metabolic enzymes. Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Aug;163(7):1479-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01166.x. PMID: 21175579; PMCID: PMC3165957.
- Nelson KM, Bisson J, Singh G, Graham JG, Chen SN, Friesen JB, Dahlin JL, Niemitz M, Walters MA, Pauli GF. The Essential Medicinal Chemistry of Cannabidiol (CBD). J Med Chem. 2020 Nov 12;63(21):12137-12155. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c00724. Epub 2020 Sep 10. PMID: 32804502; PMCID: PMC7666069.
- Bonini SA, Premoli M, Tambaro S, Kumar A, Maccarinelli G, Memo M, et al. Cannabis sativa: a comprehensive ethnopharmacological review of a medicinal plant with a long history. J Ethnopharmacol 2018; 227: 300-15.
- 10 คำถาม “กัญชง-กัญชา” เรื่องน่ารู้จาก “อภัยภูเบศร”, กรมสุขภาพจิต, 2564.
- โครงการสนับสนุนอุตสาหกรรมแปรรูปพืชกัญชง เพื่อตอบสนองเศรษฐกิจชีวภาพ (Bioeconomy) ปีงบประมาณ พ.ศ. 2564.
- บังอร ศรีพานิชกุลชัย, การใช้กัญชาเพื่อประโยชน์ทางการแพทย์, วารสารเภสัชศาสตร์อีสาน 2562; 15(4) : 1-26.
- ศรายุธ ระดาพงษ์, พราว ศุภจริยาวัตร และเมธิน ผดุงกิจ, ฤทธิ์ทางเภสัชวิทยาและพิษวิทยาของกัญชา, วารสารกรมวิทยาศาสตร์การแพทย์, 2564; 63 (1) : 219-232.
- บทความความรู้กัญชาทางการแพทย์ องค์การเภสัชกรรม.