Service Information: Biomarker Testing Service for Terpenes in Cannabis using GC Technique
VISBIO Limited Company offers a service for examining and analyzing the biological components (Biomarkers) of Terpenes in all health and beauty industry products using Gas Chromatography (GC) technique. Terpenes are a crucial group of compounds found in the extracts of cannabis and are present in various health and beauty products. Terpenes are significant components of the cannabis plant’s aromatic oils, commonly found in the flower buds. These compounds are responsible for the distinctive fragrance of cannabis. Terpenes are aromatic compounds that don’t have a direct effect on the nervous system but contribute to the overall scent of cannabis. While terpenes are prominently found in cannabis, they are also present in other plants such as pine trees, orange peels, lavender, mangoes, lemongrass, and more.
Ongoing research and studies on terpenes have been conducted extensively, aiming to utilize them in industries like cosmetics, dietary supplements, and pharmaceuticals. For instance, there is a focus on developing synthesized terpene fragrances that closely resemble the aromas of various cannabis strains. This development is intended for use in dietary supplements and other related products.
Introduction to Cannabis
Cannabis, scientifically known as Cannabis sativa L. subsp. indica (Lam.), has been used for medicinal purposes in traditional medicine for thousands of years. Its use dates back to the 8th century in the ancient Arab pharmacopeia and has also been documented in Chinese medicine, Ayurvedic medicine, Thai traditional medicine, and the pharmacopoeias of England and other countries. Cannabis is a plant that thrives well in warm climates, and it is a fast-growing, bushy plant that can reach heights of around 2-4 feet. Its leaves are palmate with serrated leaflets, resembling the leaves of hemp or maple trees. Each leaf typically consists of 5-7 leaflets on a single stalk.
Cannabis has gained legal recognition for medical and recreational use in several countries. It contains various important compounds, one of which is Cannabinoids, found mainly in the female flowering buds of the plant, within the trichomes. These compounds are often present in the form of Carboxylic acids or Acid forms, which, upon exposure to light and heat, can convert into their neutral forms. Notable Cannabinoids include THC (Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (Cannabidiol). Due to the presence of multiple Cannabinoids and other compounds like Flavonoids, Steroids, Terpenes, and Fatty acids, analyzing and quantifying these substances is complex. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a common technique used for the analysis and quality control of these compounds.
Terpenes in Cannabis
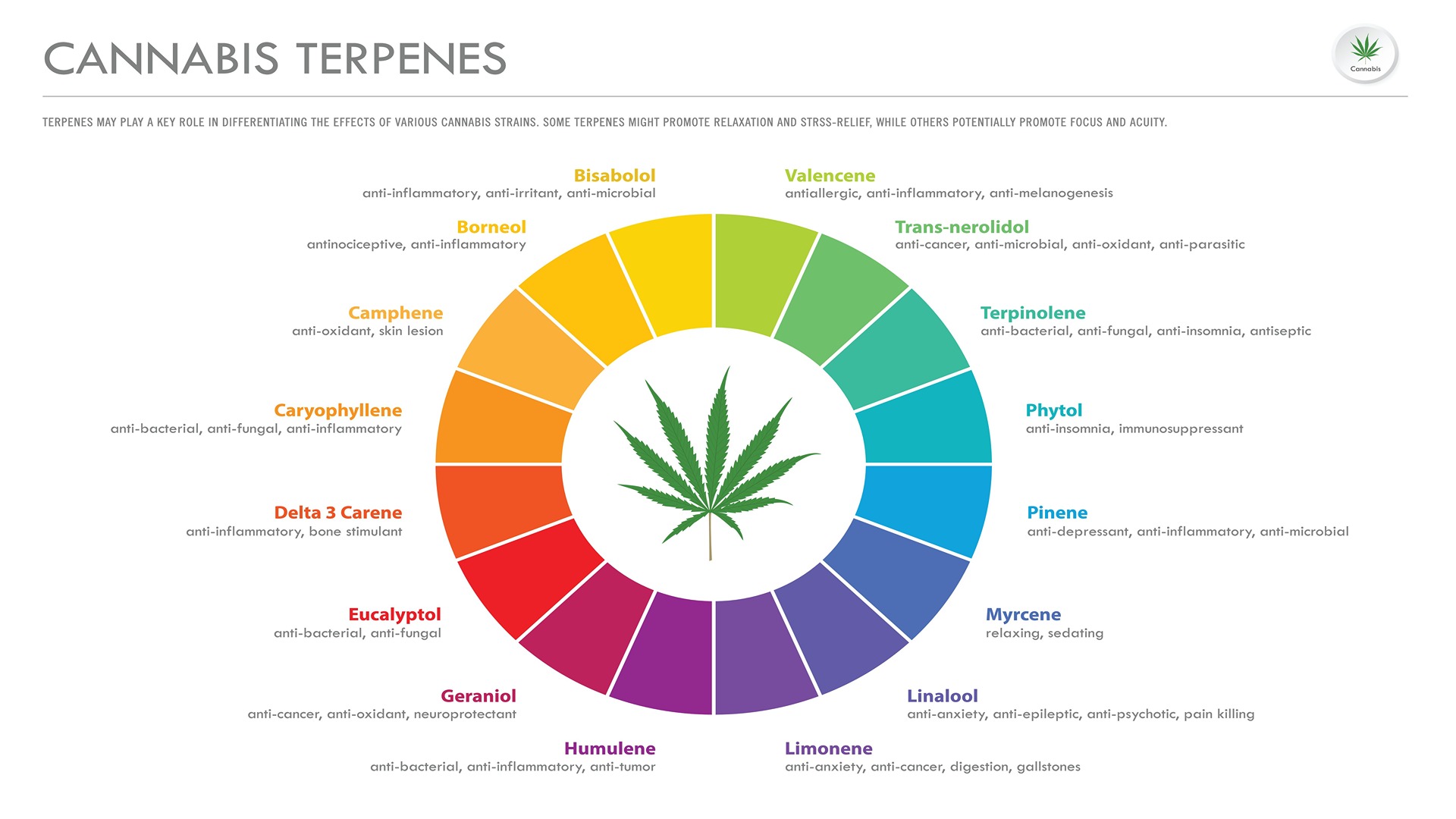
Terpenes are active ingredients found in Cannabis extracts, contributing to its aromatic properties. They are major constituents of essential oils and are responsible for the distinctive scent of Cannabis. Terpenes are not neurologically active on their own but contribute to the overall fragrance. They are also present in various other plants, such as pine, citrus fruits, lavender, and more.
Research into Terpenes has increased, aiming to utilize them in industries such as cosmetics, dietary supplements, and medicine. Terpenes in Cannabis vary between different strains and contribute to the unique scents associated with each strain. There are more than 100 types of Terpenes present in Cannabis flowers, including Limonene, Myrcene, Alpha-pinene, Beta-caryophyllene, D-linalool, and Humulene. Each strain of Cannabis may have varying quantities of these Terpenes, leading to distinct aromatic profiles. Terpenes, along with different types of Cannabinoids, contribute to the Entourage Effect, enhancing the therapeutic potential of the plant.
In summary, Cannabis is a plant with a long history of medicinal use. It contains various compounds, including Cannabinoids and Terpenes, each with their own unique effects. The study of these compounds is ongoing, and their potential benefits in various industries continue to be explored.
Analysis of Tetrahydrocannabinol Content in Cannabis Using GC Technique
When utilizing tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) compounds from cannabis in various products, it is necessary to control their quality. This is particularly important when applying them in the medical field, as using excessive or insufficient quantities could impact treatment outcomes. One of the methods commonly employed to analyze and quantify the appropriate amount of THC compounds is Gas ChromatographyMass Spectrometry (GC-MS) technique.
Gas Chromatography (GC) is a technique commonly used for separating complex mixtures that can be easily vaporized. It involves preparing samples without necessarily using organic solvents for sample extraction. This is achieved through a two-phase system comprising the stationary phase and the mobile phase. The stationary phase involves a coating or adsorbent material inside the column that separates substances. The mobile phase, typically a carrier gas like helium, nitrogen, or argon, helps carry the sample through the column. When a sample mixture is injected into the gas chromatograph at the injection port, which is heated to a temperature sufficient to convert the sample from liquid to gas, the gas phase of the sample moves through the column using the carrier gas. The column is temperature controlled, allowing separation to occur. The separated components within the column then move to the detector, such as a Mass Spectrometry unit, and the results are presented in the form of a chromatogram. This allows for identification of the substance type and comparison of sample quantities. Hence, it enables both quantitative and qualitative analysis.
Example of Reporting Test Results for THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) in Cannabis Using GC Technique
Reporting the Gas Chromatogram results of the analysis of THC extract compounds from cannabis tissue in the flowering part of the cannabis plant using the GC-MS (Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry) technique.
Literature:
- บังอร ศรีพานิชกุลชัย, การใช้กัญชาเพื่อประโยชน์ทางการแพทย์, วารสารเภสัชศาสตร์อีสาน 2562; 15(4) : 1-26.
- สุภาภรณ์ ปิติพร, กัญชาเพื่อประโยชน์ทางการแพทย์, โรงพยาบาลเจ้าพระยาอภัยภูเบศรฯ
- วีรวรรณ ลำดับศรี, การตรวจวิเคราะห์องค์ประกอบทางเคมีของสารเสพติดประเภทกัญชาเพื่องานด้านนิติวิทยาศาสตร์ ปริญญาวิทยาศาสตรมหาบัณฑิต (นิติวิทยาศาสตร์) สาขาวิชานิติ วิทยาศาสตร์คณะศิลปศาสตร์และวิทยาศาสตร์, 2563.
- Sommano SR, Chittasupho C, Ruksiriwanich W, Jantrawut P. The Cannabis Terpenes. Molecules. 2020 Dec 8;25(24):5792. doi: 10.3390/molecules25245792. PMID: 33302574; PMCID: PMC7763918.
- Ibrahim EA, Wang M, Radwan MM, Wanas AS, Majumdar CG, Avula B, Wang YH, Khan IA, Chandra S, Lata H, Hadad GM, Abdel Salam RA, Ibrahim AK, Ahmed SA, ElSohly MA. Analysis of Terpenes in Cannabis sativa L. Using GC/MS: Method Development, Validation, and Application. Planta Med. 2019 Mar;85(5):431-438. doi: 10.1055/a-0828-8387. Epub 2019 Jan 15. PMID: 30646402.




