Information about Stimulation Collagen Production Testing Service
VISBIO Co., Ltd. offers services for testing and analyzing the stimulate Collagen production in products. This service involves cultivating cells in 2D cell culture and is available for all products in the health and beauty industry or food and beverage industry.
Collagen, the most abundant fibrous protein in the body, naturally contributes to enhancing strength and flexibility in various body parts, acting like glue. Collagen is well-known for its role in nurturing skin health, reducing wrinkles, joint care, hair and nail health, among other benefits. Therefore, testing the efficacy of collagen stimulation is particularly suitable for products in the herbs, raw materials, cosmetics or dietary supplement industries that focus on collagen-related outcomes such as wrinkle reduction, skin nourishment, nail/hair care, joint care, and more. In the health and beauty industry, substances with collagen-stimulating properties are highly regarded as components in their products.
What is Collagen?
Collagen is the most abundant fibrous protein found in the body. It can be naturally synthesized and acts similarly to glue, contributing to the strength and flexibility of various body parts. Collagen makes up approximately 30% of all connective tissues and is found in blood vessels, cartilage, muscles, tendons, hair, nails and skin. The body synthesizes collagen most efficiently at a young age, and its production decreases as one gets older.
Structure and Types of Collagen.
Collagen’s structure consists of collagen fibers, which are composed of three polypeptide chains twisted together with the help of collagen cross-links. Each chain is made up of approximately 1,000 amino acids, with G representing glycine, X representing proline, and Y representing hydroxyproline (Hype).
Figure 1. The structure of collagen results from the assembly of amino acids.
Collagen is divided into 5 types as follows:
- Type I Collagen: The main collagen of the skin and bones, comprising approximately 90% of the body’s collagen. It enhances elasticity, prevents tissue from tearing, and results in smooth and flawless skin for those with high levels of this type of collagen.
- Type II Collagen: Found in cartilage and connective tissues, it plays a crucial role in stimulating cell synthesis to reduce the rate of cartilage degeneration, especially around the joints.
- Type III Collagen: Present in blood vessels and internal organs.
- Type IV Collagen: This type is found in the connective tissues that envelop muscles and fat, contributing to the proper functioning of the circulatory and nervous systems.
- Type V Collagen: Found in the skin of cells and hair.
Collagen and Dietary Supplements in Thailand
In the health and beauty industry in Thailand, collagen products come in 3 main types:
- Native Collagen: This is collagen that has not undergone the hydrolysis process, and it has properties that make it insoluble in water and less absorbent.
- Gelatin Medium-Soluble Collagen: This type of collagen has undergone hydrolysis, making it water-soluble and moderately absorbent.
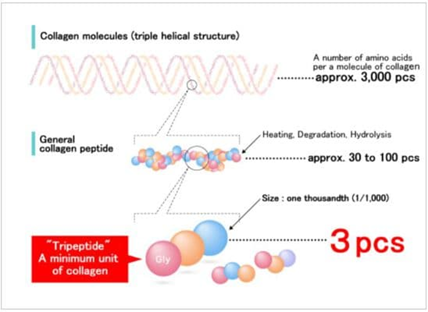
- Collagen Tripeptide (CTP): CTP is collagen that has been extensively hydrolyzed, resulting in excellent water solubility. It contains amino acids, with one of them being glycine. It has a small molecular weight and a ratio of 1/1000, allowing it to be well absorbed in the small intestine. CTP has properties that contribute to skincare and moisturizing the skin.
Figure 2. Molecular Structure of Collagen Tripeptide
Collagen Dissolution or Degradation
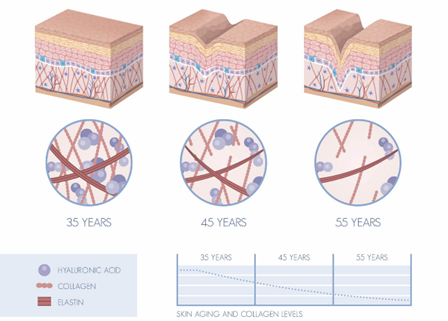
In the human body, as one ages, the production of collagen decreases. This can affect the skin, making it thinner, drier, and less elastic, leading to the development of wrinkles. Research has shown that our bodies start losing collagen from the age of 30 and onwards. The causes of collagen dissolution or degradation may be linked to factors like aging and environmental influences, which can accelerate collagen breakdown. These factors include exposure to UV radiation, pollution, and choosing to consume nutritionally deficient foods.
Figure 3. Skin Aging According to Age and Collagen Levels
Method for Testing the Stimulation of Collagen Production Under 2D Cell Culture
Testing can be performed for the ability to stimulate collagen production in 2D cell culture, which can be applied to herbs, ingredients, raw materials, extracts, herbal products, cosmetics or dietary supplements. The testing process includes the following steps: The laboratory cultivates Human Dermal Fibroblasts (HDFa) cells were cultured in an incubator and subsequently transferred into a 96-well plate, with 2500-5000 cells per well. Following a 96-hour incubation period, the cells adhered to the surface. After this incubation, the cells were collected and centrifuged to separate the cell culture medium. Both the cell culture medium and cell lines were then subjected to testing using the Sircol™ Soluble Collagen kit to quantify the Collagen content. The Collagen produced by HDFa cells was determined by comparison with standard Collagen samples.
The report testing results can be done in 2 ways:
- Testing for the efficacy of stimulating collagen production, which determines whether the sample product has properties that stimulate collagen production.
- Reporting test results by calculating the half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50), which measures the sample’s concentration needed to stimulate 50% of collagen production, comparing it to a standard substance. This type of reporting is suitable for raw material samples such as herbs and extracts, which are used in the development of various health and beauty products or food and beverage products.
Literature:
- ดร.ฉัตรภา หัตถโกศล (DrPH, RD) อาจารย์ประจําภาควิชาโภชนวิทยา คณะสาธารณสุขศาสตร์มหาวิทยาลัยมหิดล
- วารสารวิจัยและพัฒนา มจธ ปีที่ 42 ฤทธิ์ต้านอนุมูลอิสระและต้านริ้วรอยของสารสกัดข้าวทับทิมชุมแพสำหรับประยุกต์ ใช้ในเครื่องสำอางบำรุงผิวหน้า
- Researchers, Inquiry about collaborative research ‘’What is Collagen Tripeptide”
- Researchers, Vibrance skin rejuvenation medspa ‘’What happens to collagen as we age’ April 3, 2020
- Shoulders, M., and Raines, R. Collagen Structure and Stability. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009. vol. 78, p. 929-958