Service Information about Quantitative Vitamin B12 Testing in herbs or products using HPLC technique.
VISBIO provides a service for the examination and quantitative analysis of the biological component (Biomarker) of Vitamin B12, in herbs or products across the health and beauty industries or food and beverage industries.
Vitamin B12 is essential for red blood cell production, normal functioning of the nervous system, brain, and immune system. It is generally not found in plant-based foods, making individuals adhering to strict vegetarian diets susceptible to Vitamin B12 deficiency. Consequently, there is an abundance of Vitamin B12 supplements in various products today. Therefore, it is crucial to test and control the quality of Vitamin B12 in products or analyze its presence in sample specimens such as plasma, serum, and urine. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a widely used technique for this analysis.
What is Vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12, also known as Cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin that contains the mineral cobalt (Co) as a component. Vitamin B12 is unique among vitamins because it contains a mineral as a component and has a highly complex, large molecular structure. Although the body requires it in small quantities, it is essential because Vitamin B12 plays a crucial role in various important enzymes’ functioning, such as Methionine synthase and Methyl malonyl CoA mutase. Generally, plants and animals cannot synthesize Vitamin B12, but it is produced by bacteria in the large intestine.
Sources of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is found in foods of animal origin, including meat, organ meats, eggs, dairy products, but not in plant-based foods. Therefore, individuals who follow strict vegetarian diets and do not consume any animal products, such as meat, eggs, or dairy, are at risk of Vitamin B12 deficiency. Hence, it is advisable for them to take Vitamin B12 supplements in the form of fortified foods or dietary supplements.
Benefits of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 offers numerous health benefits, including:
- Assisting in the production of red blood cells.
- Supporting the normal functioning of the nervous system and brain.
- Providing the body with energy by aiding in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
- Playing a role in maintaining a healthy immune system.
Vitamin B12 Requirements for the Body
The body’s vitamin B12 requirements vary across different age groups as follows:
- Individuals aged 19 years and older, as well as seniors, should aim to consume 2.4 micrograms of vitamin B12 per day.
- Pregnant women and those who are breastfeeding should increase their daily vitamin B12 intake to 0.2 and 0.4 micrograms, respectively.
A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, confusion, and megaloblastic anemia, a condition where red blood cells are larger than normal (Megaloblastic anemia). Additionally, strict adherence to a vegan diet during pregnancy can increase the risk of vitamin B12 deficiency in the developing fetus, potentially affecting brain development, memory, and learning abilities.
The Use of Vitamin B12 in the Food Industries
Currently, health beverages or functional drinks that contain vitamin B12 or are combined with other vitamin B such as fruit juices, vitamin water, and energy drinks, are widely available in the market. These products are popular among health-conscious consumers who prefer convenient and tasty options to traditional vitamin supplements in pill or capsule form. The development of health beverages with added vitamin B12 provides consumers with an easy, delicious, and quick way to support their health.
The Use of Vitamin B12 in the Nutritional Supplements and Pharmaceutical Industries
Vitamin B12 is also used in the development of nutritional supplements and pharmaceutical products. It is often combined with other vitamins like B1, B6, and B12 or with various minerals as part of multivitamin and mineral supplements to prevent vitamin deficiencies.
In the case of pharmaceutical products, vitamin B12 is typically present in higher concentrations compared to dietary supplements. These pharmaceuticals may come in the form of tablets or injections and are used to treat conditions such as megaloblastic anemia, peripheral neuropathy in diabetic patients, or to alleviate the symptoms of nerve damage.
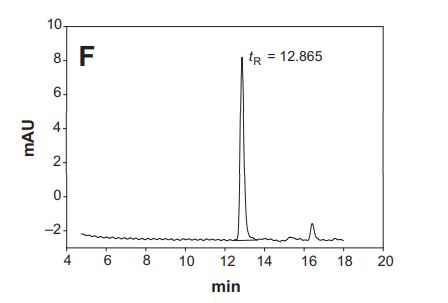
Example of Vitamin B12 Analysis Report Using HPLC Technique
The graph shows the chromatogram of vitamin B12 in a fortified cereal, which can be used to calculate the quantity of vitamin B12 by comparing it to the standard substance.
Literature:
- ประกาศสำนักงานคณะกรรมการอาหารและยา เรื่อง การแสดงข้อความกล่าวอ้างหน้าที่ของสารอาหาร, เล่ม 136, 10 มิถุนายน 2562.
- ปริมาณสารอาหารอ้างอิงที่ควรได้รับประจำวันสำหรับคนไทย พ.ศ.2563 โดย คณะกรรมการและคณะทำงานปรับปรุงข้อกำหนดสารอาหารที่ควรได้รับประจำวันสำหรับคนไทย สำนักโภชนาการ กรมอนามัย กระทรวงสาธารณสุข.
- Harvard T.H. Chan, The Nutrition Source, Vitamin B12, https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/vitamin-b12/
- Jessy van Wyk, Trevor J. Britz. A rapid HPLC method for the extraction and quantification of vitamin B12 in dairy products and cultures of Propionibacterium freudenreichii. Dairy Science & Technology, 2010, 90 (5), ff10.1051/dst/2009055ff.
https://www.mims.com/Thailand/drug/search/?q=mecobalamin